Figure 4.
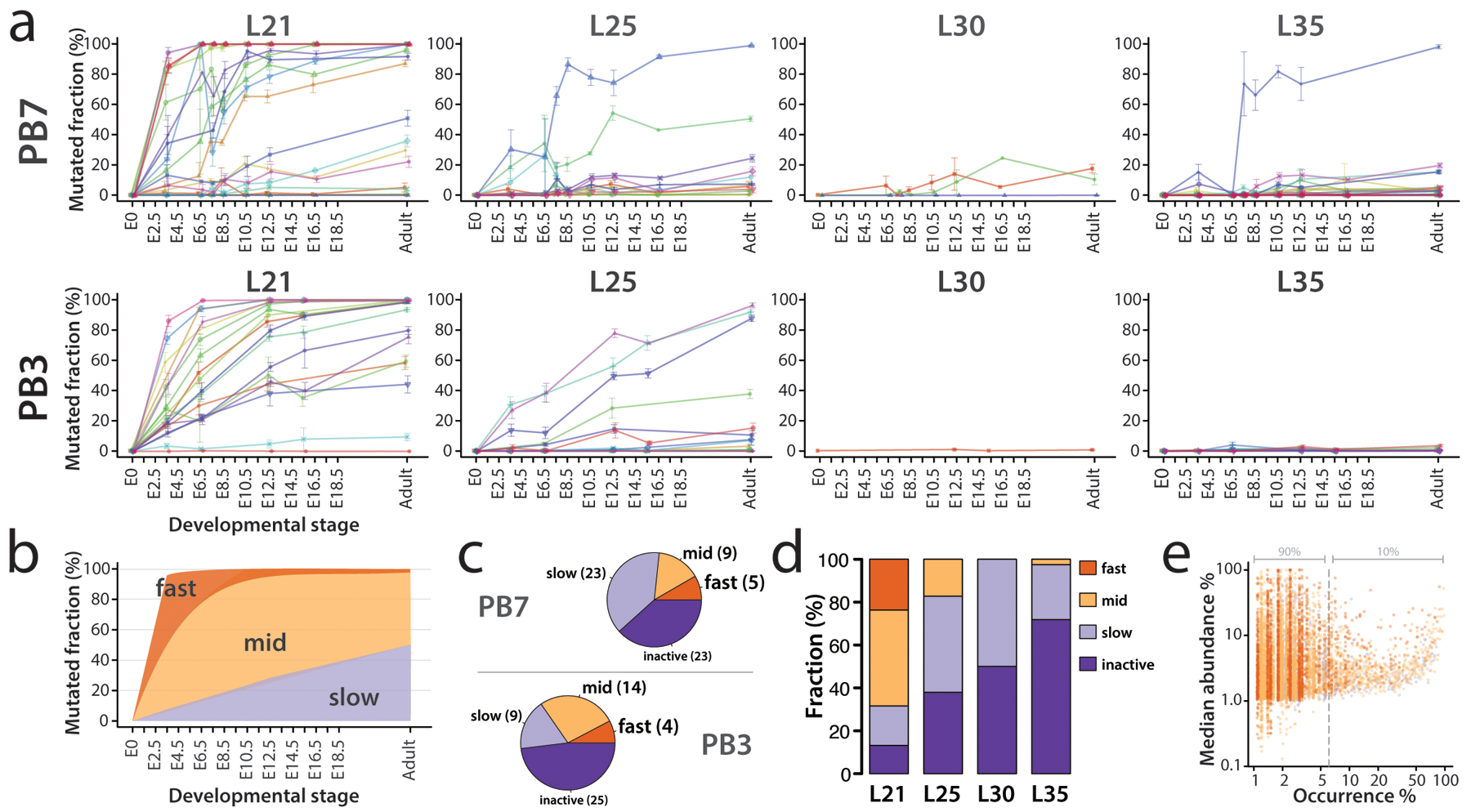
Activity of MARC1 hgRNAs. (a) Activity profiles of all 60 PB7 and 54 PB3 hgRNAs in embryonic and adult progenies of the MARC1 founder crossed with Cas9 knock-in females, broken down by hgRNA length. The fraction of mutated spacers in each hgRNA was measured. Lines connect the observed average mutation rates of the same hgRNA at different timepoints. Means ± SEMs are shown (N is different for each value; see Supplementary Table 2). See Supplementary Table 3 for numerical values of the plot. Adult mice were sampled via ear punch at 21 days old. (b) Range of activity profiles of each hgRNA class across progeny of both MARC1 founders crossed with constitutive Cas9 knock-in females. (c) The breakdown of hgRNA classes in the PB7 and PB3 lines; parentheticals represent absolute counts of each class. (d) Classification of combined PB3 and PB7 hgRNAs based on their activity profile in (a), broken down by length. (e) Observed distribution of all mutant alleles for all MARC1 hgRNAs shows that a majority of mutant alleles are unique. Each dot represents an observed mutant allele of a given hgRNA. Results for the combined set of all 112 hgRNAs are overlaid. The x-axis corresponds to the percentage of mice in which a specific allele was observed. The y-axis corresponds to the abundance of each allele when present. For example, a value of (5%, 10%) would indicate that a given mutant allele was observed in 5% of all barcoded mice inheriting the corresponding hgRNA identifier and with an abundance of 10%, on median. Dots are colored based on hgRNA activity profiles in accordance with the color key in d. Supplementary Table 4 contains the numeric breakdown for all observed alleles. L21, L25, L30, L35: hgRNAs with spacers of length 21, 25, 30, and 35 bases respectively. Top row of plots in panel a is adapted from ref. 7 with permission.
