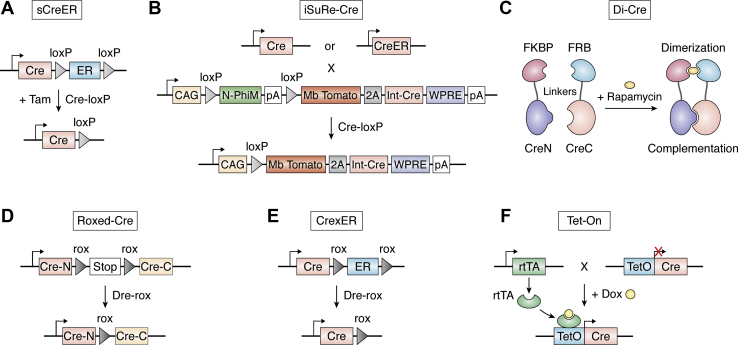
Figure 2.
Chemical-inducible recombination systems.A, a self-cleaved inducible CreER (sCreER) with a Cre-loxP-ER-loxP construct that switches inducible CreER into a constitutively active Cre by itself once tamoxifen induction. B, the iSuRe-Cre is an inducible dual reporter-Cre, containing CAG promoter, N-PhiM and MbTomato reporter gene, and a constitutively active and permanently expressed Cre. After removal of the floxed N-PhiM cassette by Cre or CreER, iSuRe-Cre co-expresses MbTomato and a constitutively active Cre and significantly increases the efficiency and certainty of gene deletion in reporter-expressing cells. C, the DiCre in which Cre is split into two inactive moieties and fused with FKBP12 and FRB respectively. FKBP12 and FRB can be heterodimerized efficiently after rapamycin treatment, leading to the complementation of inactive fragments (CreN and CreC) and Cre activity restoration. D, the Roxed-Cre contains a Cre-N-rox-stop-rox-Cre-C construct. The reinstatement of Cre activity occurs after the removal of the rox-flanked STOP cassette by Dre-rox recombination. E, the CrexER with a Cre-rox-ER-rox construct executes Cre activity after the removal of ER by Dre-rox recombination. F, the Tet-On inducible system consists of two transgenes, a recombinase under the control of a TRE and a rtTA driven by a cell-specific promoter. After Dox administration, the rtTA is active and interacts with the TetO promoter. CreC, the C-terminal domain of Cre; CreN, the N-terminal domain of Cre; DiCre, dimerizable Cre; Dox, doxycycline; FKBP12, FK506-binding protein; FRB, binding domain of the FKBP12-rapamycin associated protein; rtTA, reverse tet-controlled transactivator; Tam, tamoxifen; TRE, Tet responsive element.