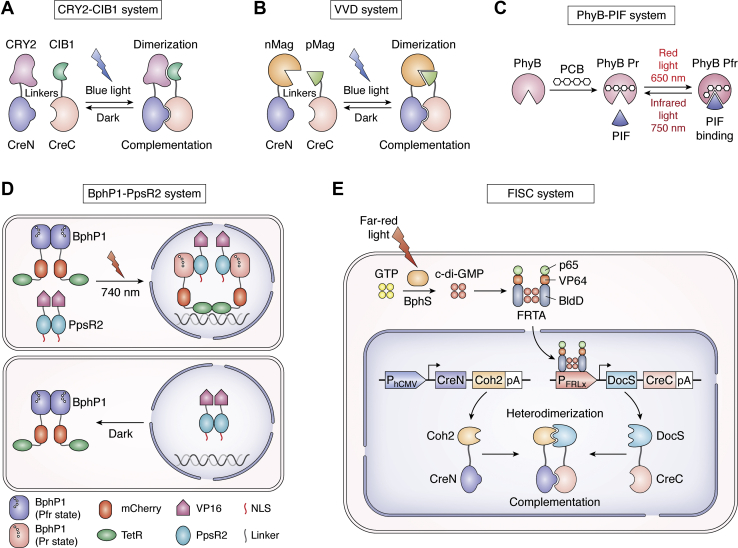
Figure 4.
Genetically encoded light-inducible recombination systems.A, CRY2 and the N terminus of CIB1 are fused to the CreN and CreC, respectively. Upon the illumination of blue light, the dimerization of CRY2 and CIBN leads to the reconstitution of split Cre recombinase activity. B, the photoreceptor Vivid (VVD) is designated as Magnets and comprises two photoswitches named pMag and nMag. The heterodimerization of pMag and nMag induced by the blue light illumination leads to the complementation of CreN and CreC and Cre activity reconstitution. C, the PhyB absorbs red and infrared light through the photoisomerization of a covalently bound PCB. The conformation of PhyB changes between the Pr (red-absorbing) and Pfr (far-red-absorbing) states catalyzed by red and infrared light. The PIF only associates with PhyB in Pfr state. The heterodimerization between PhyB and PIF is reversibly triggered by red (650 nm) and infrared (750 nm) light. D, a light-inducible transcription activation system based on BphP1-PpsR2 and TetRtetO. BphP1-mCherry and the C terminus of NLS-PpsR2 are fused to the TetR and VP16, respectively. Upon near-infrared light illumination, BphP1 converts into the Pr state and forms heterodimer with PpsR2. NLS facilitates the heterodimer translocates to the nucleus where BphP1 fusions interact with tetO DNA repeats via TetR. VP16 recruits the transcription initiation complex and triggers gene transcription. E, the FISC system is designed on the basis of the affinity of bacteriophytochrome Coh2 and DocS. In this system, DocS-CreC fusion protein is under the control of FRL-inducible promoter PFRL, CreN fused to Coh2 driven by a constitutive promoter PhCMV. Upon FRL exposure, the active photoreceptor BphS converts GTP into c-di-GMP which induces binding of FRTA (p65-VP64-BldD) to promoter PFRL to drive DocS-CreC expression. The interaction of Coh2 and DocS domains leads to the reunion of CreC and CreN and Cre activity reinstatement. c-di-GMP, cyclic diguanylate monophosphate; CreC, the C-terminal domain of Cre; CreN, the N-terminal domain of Cre; CRY2, cryptochrome 2; FISC system, far-red light-induced split Cre-loxP system; FRL, far-red light; FRTA, far-red light-dependent transactivator; GTP, guanylate triphosphate; NLS, nuclear localization signal; nMag, negative Magnet; PCB, chromophore phycocyanobilin; PhyB, photoreceptor phytochrome B; PIF, phytochrome interaction factor; pMag, positive Magnet; TetR, tetracycline repressor.