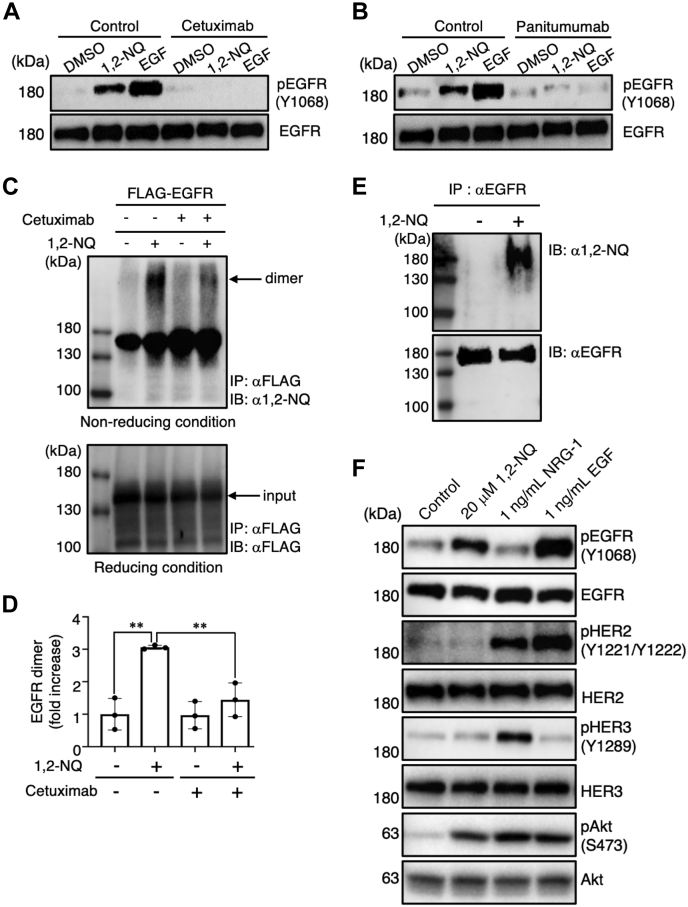
Figure 2.
1,2-NQ directly induces EGFR dimerization and tyrosine phosphorylation.A and B, A549 cells were incubated with serum-free medium for 24 h and were then exposed to 10 μM 1,2-NQ or 10 ng/ml EGF for 10 min. Cells were pretreated with cetuximab (A) or panitumumab (B) for 3 h before stimulation with 1,2-NQ or EGF. C, human embryonic kidney 293T cells were transiently transfected with pIDT-SMART (C-TSC) human EGFR-FLAG. Cells were incubated with serum-free medium for 18 h and were then exposed to 10 μM 1,2-NQ for 10 min. Cells were pretreated with cetuximab for 3 h before stimulation with 1,2-NQ. Immunoprecipitation was performed under nonreducing conditions for the detection of EGFR dimerization (upper) and under reducing conditions for input analysis (lower). Western blotting was conducted with anti-1,2-NQ or anti-FLAG antibodies. D, quantification of 1,2-NQ–induced EGFR dimerization in A549 cells. The relative level of EGFR dimers was normalized to the input EGFR level and shown as a fold change compared with the control. Statistical analysis was carried out by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test. All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM values. n = 3, ∗p < 0.05, and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control. E, A549 cells were cultured with serum-free medium for 24 h before exposure to 10 μM 1,2-NQ for 10 min. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoprecipitation using an anti-EGFR antibody and by Western blotting with anti-1,2-NQ or anti-EGFR antibodies. F, A549 cells were incubated with serum-free medium for 24 h and were then exposed to 20 μM 1,2-NQ, 1 ng/ml EGF, or 1 ng/ml NRG-1 for 10 min. 1,2-NQ, 1,2-naphthoquinone; Akt, protein kinase B; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HER, human epidermal growth factor receptor; NRG-1, neuregulin-1.