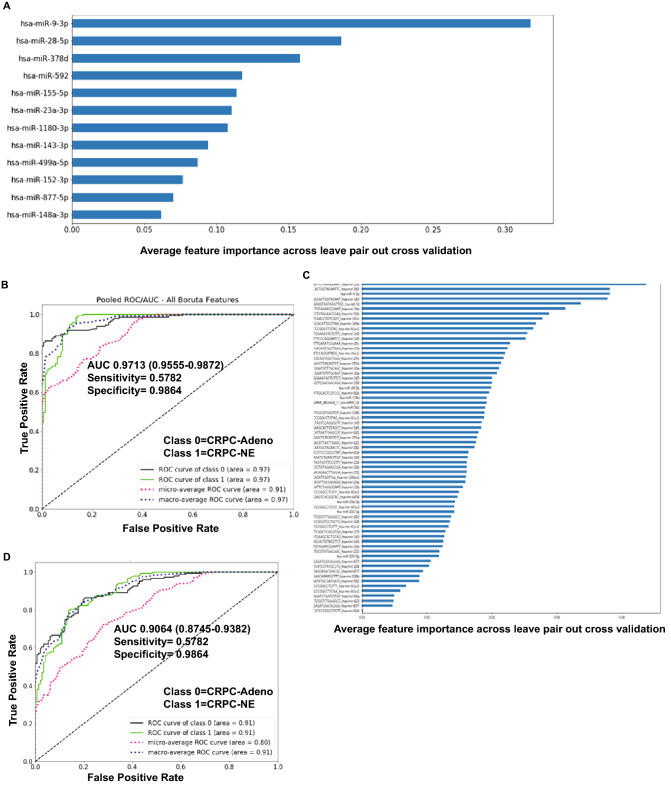
Figure 3.
An EV-microRNA classifier of neuroendocrine differentiation in castration resistant prostate cancer. (A) Application of machine learning methods (random forest machine learning technique with leave-pair-out cross validation) to the NGS dataset of analyzed NE tissues + NCI-H660 cell line (CRPC-NE, n = 7) vs those with adenocarcinoma features (CRPC-Adeno, n = 21) yielded a ‘12 miRNA classifier’. miRNAs are listed in the order of feature importance as determined by these methods. (B) ROC curve analyses showing the ability of ‘EV-miRNA classifier’ to distinguish between class 0 (CRPC-Adeno) and class 1 (CRPC-NE). (C) An EV- miRNA classifier including isoforms of miRNAs as determined by random forest machine learning technique with leave-pair-out cross validation as applied to the NGS dataset of analyzed EVs from CRPC-NE (n = 6) + NCI-H660 cell line vs those from CRPC-Adeno patients (n = 21) including miRNA isoforms. miRNAs are listed in the order of feature importance. (D) ROC curve analyses showing the ability of ‘EV-miRNA classifier including iso-miRs’ to distinguish between class 0 (CRPC-Adeno) and class 1 (CRPC-NE).