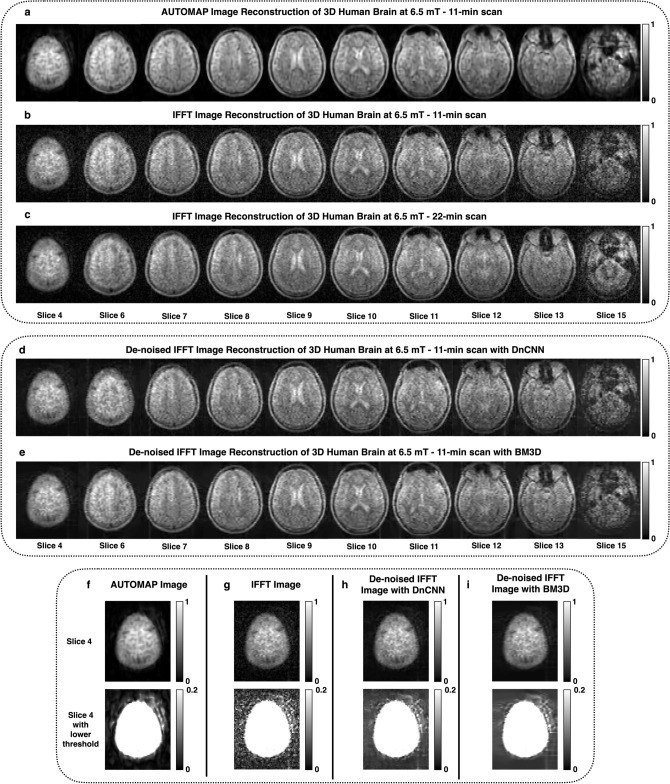
Figure 2.
3D brain image reconstruction at 6.5 mT using AUTOMAP compared to conventional IFFT with or without additional image-based denoising pipelines. (a–c) Reconstruction of 3D human head dataset—an 11-min (NA = 50) 3D acquisition dataset was reconstructed with AUTOMAP (a) and IFFT (b). Shown here are 10 slices from the full 15 slice dataset. For comparison, a 22-min (NA = 100) acquisition reconstructed with IFFT is shown in (c). The window level is unchanged in all images. (d,e) The two denoising algorithms (DnCNN and BM3D respectively) were applied to the IFFT reconstructed brain image (magnitude only) to compare to the denoising performance of AUTOMAP. (f–i) Noise floor comparison—Slice 4 from the NA = 50 reconstructed brain dataset shown above in (a,b) is displayed here with two different window levels: a normalized image on the top and a window level chosen to highlight the noise at the bottom. AUTOMAP is shown in (f), and IFFT is shown in (g). An additional DnCNN or BM3D image denoising step was applied to the image data reconstructed with IFFT (h,i respectively).