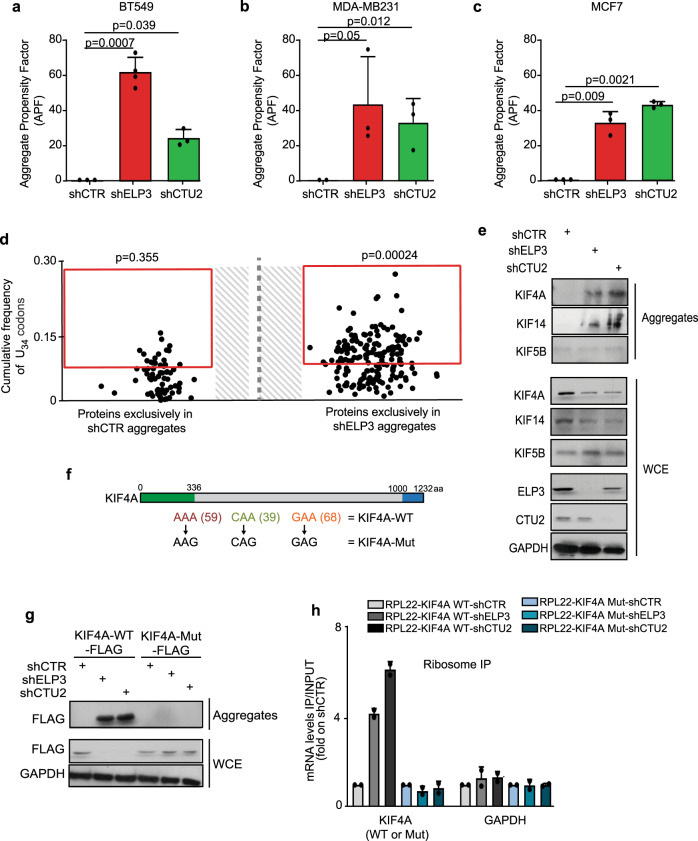
Fig. 3. Loss of U34-enzymes leads to protein aggregation in a codon-dependent manner.
a–c Protein aggregation was measured by FACS in BT549 (a), MDA-MD231 (b), and MCF7 (c) upon loss of ELP3 or CTU2 (n = 3 independent experiments, two-tail t-test, data are mean + s.d). d Protein content of aggregates of MCF7 cells depleted or not of ELP3 were assessed by proteomics (n = 1 independent experiment); proteins exclusively found in shELP3 or shCTR conditions are shown. Enrichment of U34-codons was assessed by χ2 test (two-sided). e Levels of indicated proteins were determined by western blot in whole-cell extracts (WCE; loaded 30 μg) and aggregates (isolated from >1 mg of protein extract) of MCF7 cells depleted of ELP3 or CTU2 (n = 2 replicates). f Schematic representation of KIF4A mutant. The kinesin domain (green) and the globular region (blue) of the protein are indicated. g Protein levels of whole-cell extracts (WCE) and aggregates of MCF7 cells stably overexpressing FLAG-RPL22 and the identified KIF4A mutants in the presence or absence of ELP3 or CTU2 (n = 3 replicates). h qRT-PCR after ribosome immunoprecipitation of indicated cells. n = 2 independent experiments, data are mean + s.d.