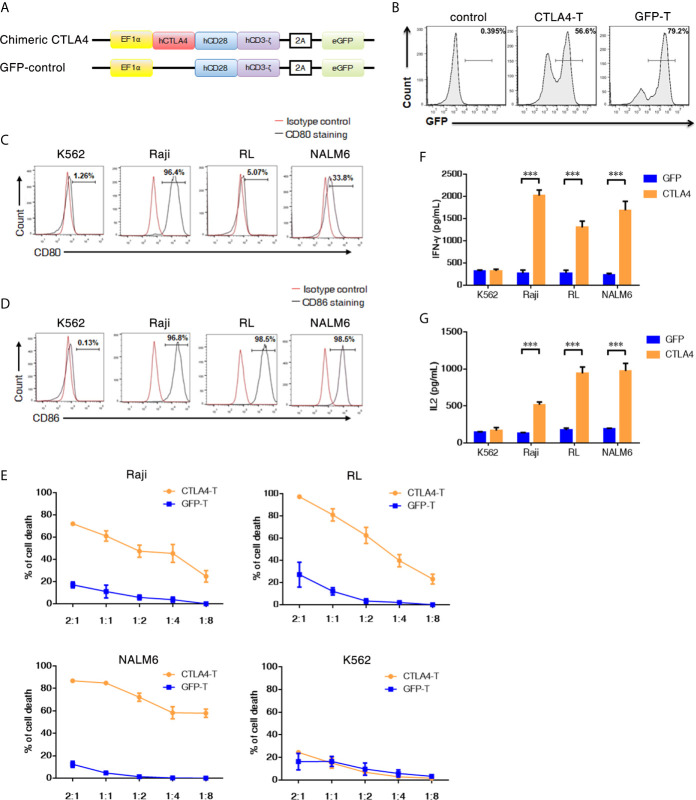
Figure 1.
T cells transduced with the CTLA4-CD28-CD3z chimeric gene showed enhanced in Vitro Cytotoxicity. (A) The chimeric CTLA4 molecule contains the extracellular and transmembrane domains of human CTLA4, the cytoplasmic signaling region of human CD28, and the intracellular domain of human CD3z. GFP was used to fluorescently label the cells. (B) Representative flow cytometric analysis of the transduction efficiency of chimeric CTLA4 or GFP (control) in human activated T cells that were transduced with a lentivirus. CTLA4-T: CTLA4 chimera-transduced T cells, GFP-T: GFP-transduced T cells. (C, D) Representative flow cytometric analyses of CD80/CD86 expression in K562, Raji, RL, and NALM6 cells. (E) Activated T cells transduced with either chimeric CTLA4 or GFP (control) and cocultured with the indicated cell lines for 18 h, mean ± SD. The levels of IFN-γ (F) and IL-2 (G) secreted into the culture supernatant were measured by ELISA with a 1:1 E:T ratio, mean ± SD, unpaired two-tailed t-test. Significance values: ***P < 0.001.