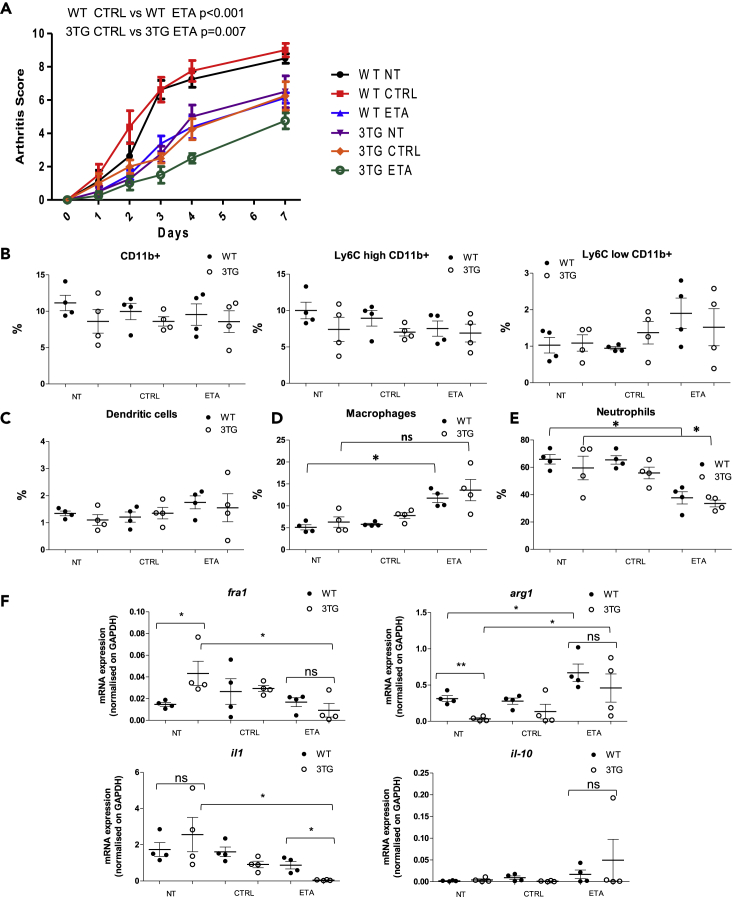
Figure 6.
tmTNF reverse signaling impact on immune cells and inflammation in arthritic joints
Eight-week-old 3TG or WT mice were injected at days 0 and 2 intraperitoneally with 200 μL of 60-week-old K/BxN mice serum to induce arthritis. Mice were injected with 10 mg/kg of anti-TNF (ETA) or control IgG1 (CTRL) 5 and 3 days prior to inducing arthritis with the first injection of KBxN serum and at days 0, 2, 4, and 7. Mice were sacrificed at day 7, and joints were dissected.
(A) Clinical effect of ETA or CTRL on the development of arthritis (arthritic score) in the WT (left panel) or 3TG (right panel) K/BxN serum-transferred mice (n = 4 per group). Control (CTRL): untreated K/BxN serum-transferred mice. Results are presented as mean arthritic score during 7 days after K/BxN injection. Data represent mean ± SEM. p value for arthritis score was calculated by repeated measurements of two-way ANOVA tests.
(B–E) Flow cytometry analysis of percentage of monocytes (B), dendritic cells (C), macrophages (D), and neutrophils (E) in joints.
(F) RT-qPCR analysis of Fra-1, Arg-1, IL-1β, and IL-10 mRNA expression. Data represent mean ± SEM of percentage of leaving cells or mRNA expression normalized on GAPDH (n = 4, ns p > 0.05, ∗p < 0.05 as calculated with Mann-Whitney U test).