Figure 2.
Deep proteome analysis to study the impact of Cbl/Cbl-b on long-term RTK signaling responses in SH-SY5Y cells
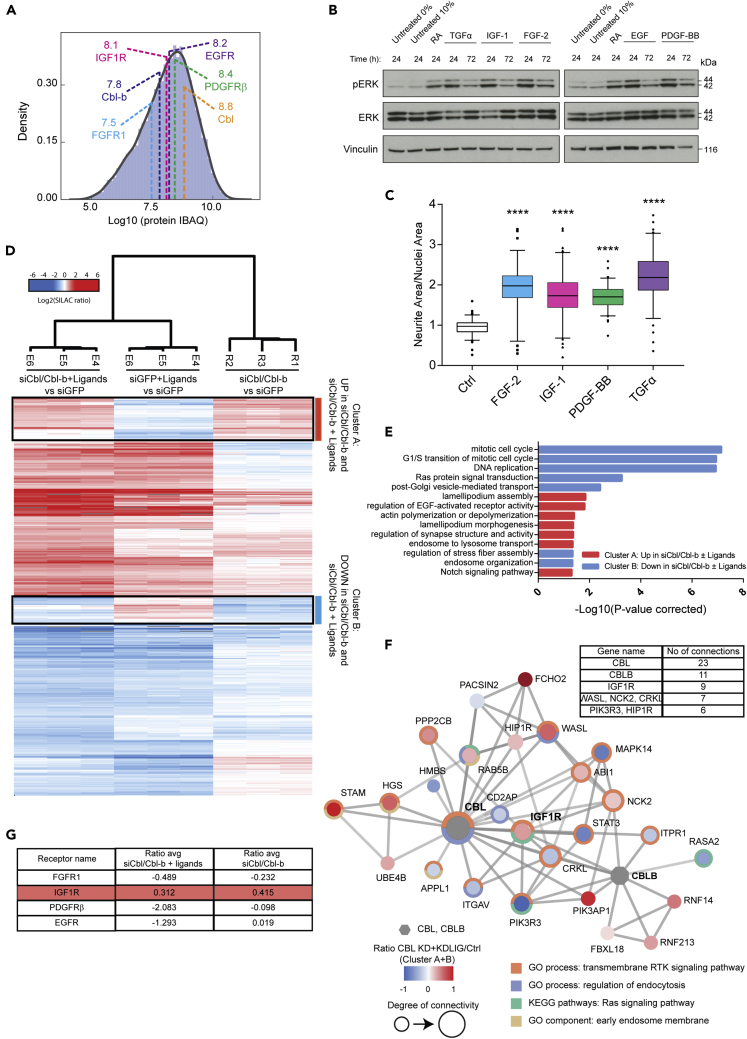
(A) Density analysis of protein abundances (IBAQ) in SH-SY5Y cells highlighting Cbl/Cbl-b and RTKs, shown with their corresponding IBAQ values (Log10).
(B) Immunoblotting for phospho-ERK of lysates from SH-SY5Y cells stimulated with FGF-2, IGF-1, PDGF-BB, or TGFα (or EGF). RA was used as a positive control.
(C) Neurite outgrowth quantification of cells exposed to the same conditions as in (B). Data are shown as medians with 95% CI. ∗∗∗∗ indicates p < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA) compared to the control. Data are representative of n = 3 independent experiments.
(D) Hierarchical clustering of proteins with significantly regulated abundance (ANOVA) in response to treatment with Cbl/Cbl-b siRNA (72 hr) and/or RTK ligand cocktail (FGF-2, IGF-1, PDGF-BB, and TGFα; 48 hr). The two clusters selected for further analyses are highlighted. Data are presented with log2 SILAC ratios all relative to siGFP control.
(E) Bar graph illustrating significantly overrepresented GO terms for biological process (GOBP) for cluster A (red) and B (blue).
(F) Functional network analysis of proteins in clusters A and B, displaying first degree connections of Cbl and Cbl-b (gray). Node color indicates regulation on protein level and surrounding colored circles indicate enriched GO terms and KEGG pathways (see legend). The table summarizes the number of connections for the most connected proteins.
(G) Table summarizing average ratios from the proteome data (relative to the siGFP control) for the RTK panel.