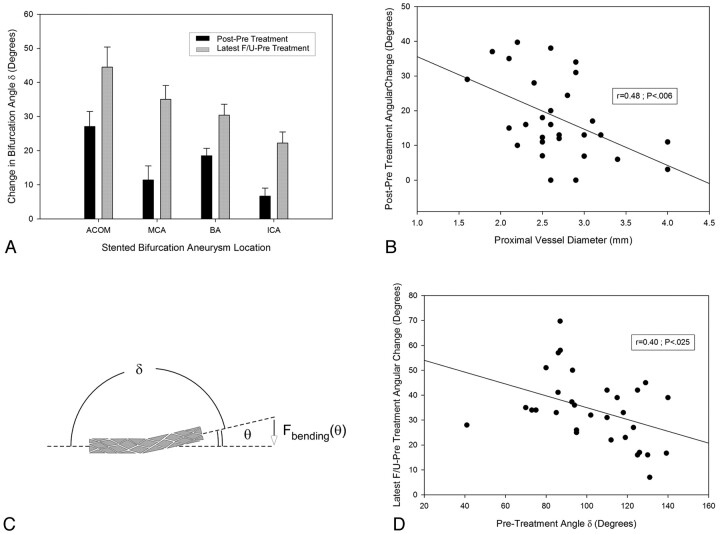
Fig 2.
A, Dependence of immediate and delayed stent-induced angular remodeling on bifurcation location. B, An inverse linear relationship between the proximal vessel diameter and the stent-induced change in angle δ. C, The relationship between the angle δ, the bending angle θ (θ = 180°− δ), and the stent-reactive force Fbending(θ). D, The inverse linear dependence of ultimate angular remodeling on the pretreatment angle δ, suggesting a link to the stent bending force.