Figure 7. Jab1 positively regulates MED1 transcriptional function by mediating its ubiquitination status.
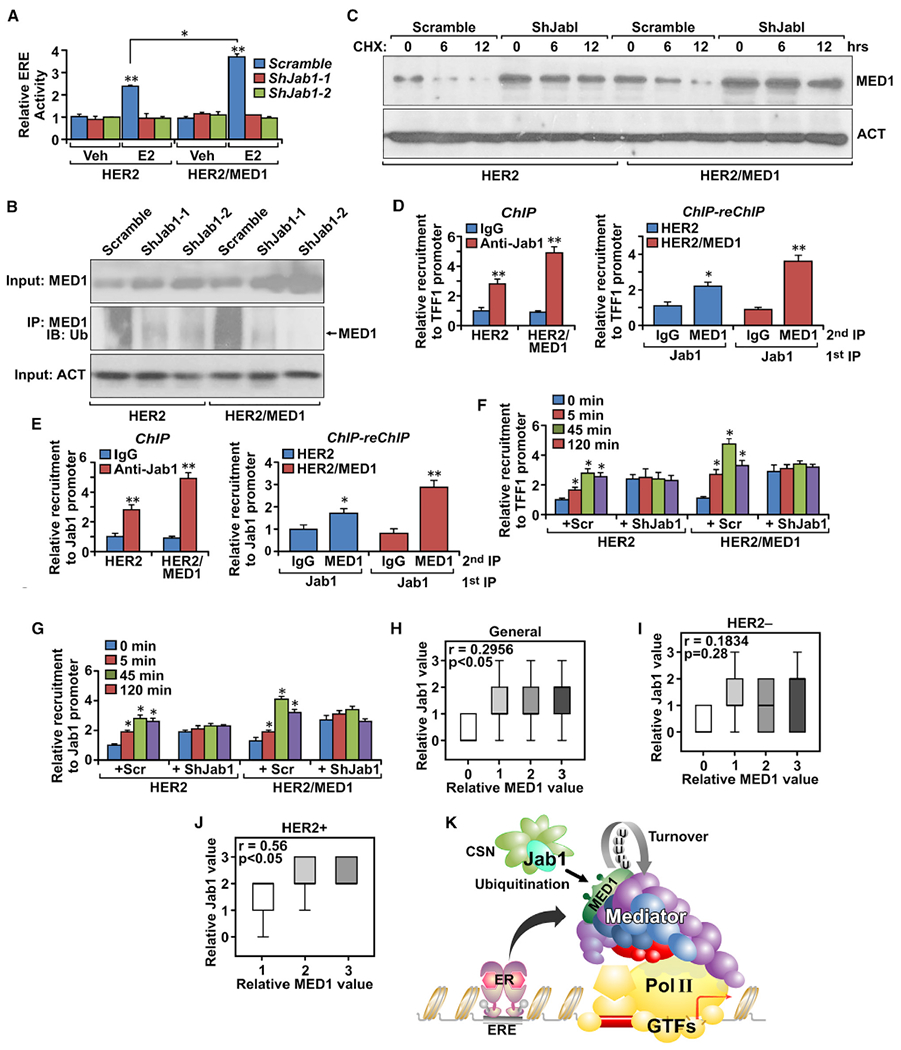
(A) ERE-luciferase assays of MMTV-HER2 and MMTV-HER2/MMTV-MED1 tumor cells transfected with Scramble or two independent shRNAs against Jab1.
(B) Immunoprecipitation and western blots analysis of MED1 ubiquitination in MMTV-HER2 and MMTV-HER2/MMTV-MED1 tumor cells transfected with Scramble or two independent shRNAs against Jab1. Total MED1 and Actin proteins in the input were also analyzed.
(C) Western blot analysis of MED1 protein level in MMTV-HER2 and MMTV-HER2/MMTV-MED1 tumor cells transfected with Scramble or two independent shRNAs against Jab1 and treated with cycloheximide (50 μg/mL) for indicated durations.
(D and E) ChIP and ChIP-reChIP analyses of Jab1 recruitment and its co-existence with MED1 at the promoter region of two MED1 target genes TFF1 (D) and Jab1 (E).
(F and G) ChIP analyses of MED1 promoter recruitment on TFF1 (F) and Jab1 (G) genes using MMTV-HER2 and MMTV-HER2/MMTV-MED1 tumor cells transfected with Scramble or shRNA against Jab1.
(H–J) Correlation of MED1 with Jab1 protein levels in the total (n = 52) (H), HER2− (n = 37) (I), and HER2+ (n = 15) (J) breast cancer clinical samples.
(K) Diagram for the interplay between MED1 and Jab1. The values are obtained from three independent experiments and shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
