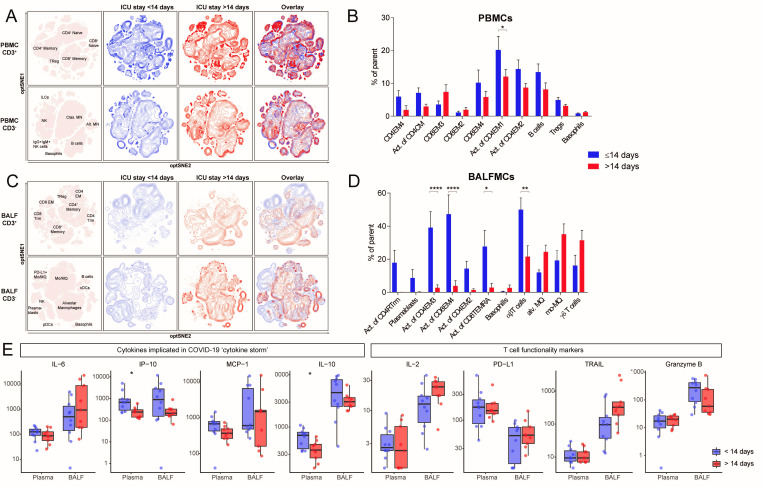
Figure 4.
Reduced T cell activation in both BALF and peripheral blood of patients with an ICU stay of >14 days. samples were stratified based on moment of sampling in ≤14 days (n=8) and >14 days (n=9). Only one sample per patient was included per group. Immune cell population from PBMCs (A) and BALFMCs (C) were clustered using omiq unsupervised clustering and presented as optSNE plots. The ten populations with biggest relative differences (sorted from left to right) are depicted for PBMC (B) and BALFMC (D). cytokine levels in plasma and BALF, as measured using Luminex, were compared ≤14 days and >14 days of ICU stay wherein box plots represent median ±interquartile range (E). Alv, alveolar; BALFMC, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid mononuclear cells; cDC, conventional DC; CM, central memory T cells; DC, dendritic cell; EM, effector memory T cells; ICU, intensive care unit; ILC, innate lymphoid cells; MN, monocyte; Mo/MQ, monocyte-like macrophage; NK, natural killer cells; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; pDC, plasmacytoid DC; TEMRA, RA+ effoctor memory T cells; Treg, regulatory T cells; Trm, tissue-resident memory T cell. Statistical significance was tested with multiple testing correction using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (B, D) or Mann-Whitney U test (E). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.