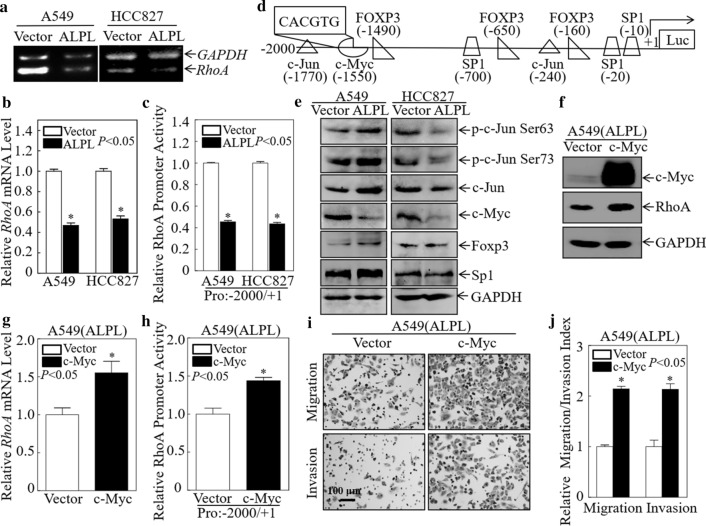
Fig. 5.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALPL) inhibits RhoA mRNA transcription by downregulating c-Myc. a Semi-quantitative PCR was used to evaluate RhoA mRNA expression after ALPL overexpression in A549 and HCC827 cells. b RhoA mRNA expression was evaluated by qPCR after ALPL overexpression in A549 and HCC827 cells. c Dual-luciferase reporter assays were used to detect RhoA promoter activity after ALPL overexpression in A549 and HCC827 cells. d TFANSFAC Transcription Factor Binding Sites Software (Biological Database, Wolfenbuttel, Germany) was used for bioinformatics analysis of the RhoA promoter region. Transcription factors for which potentially conserved binding sites were identified in the RhoA promoter region included c-Myc, c-Jun, Foxp3, and Sp1. e Western blot analysis of cell lysates from the indicated cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control. f Western blot analysis of c-Myc and RhoA expression in A549 (ALPL) cells stably transfected with c-Myc or a control plasmid. GAPDH was used as a loading control. g The RhoA mRNA expression level was evaluated by qPCR after overexpression of c-Myc in A549 (ALPL) cells. h Dual-luciferase reporter assays of the RhoA promoter activity after overexpression of c-Myc in A549 (ALPL) cells. i Transwell assays to determine the effect of overexpression of c-Myc on A549 (ALPL) cells, Scale bars: 100 µm. j The migration and invasion rate of A549 (ALPL) cells. All results were presented as the mean ± SD and analyzed by Student’s t-test, n = 3. Asterisks (*) represent statistical significance (P < 0.05)