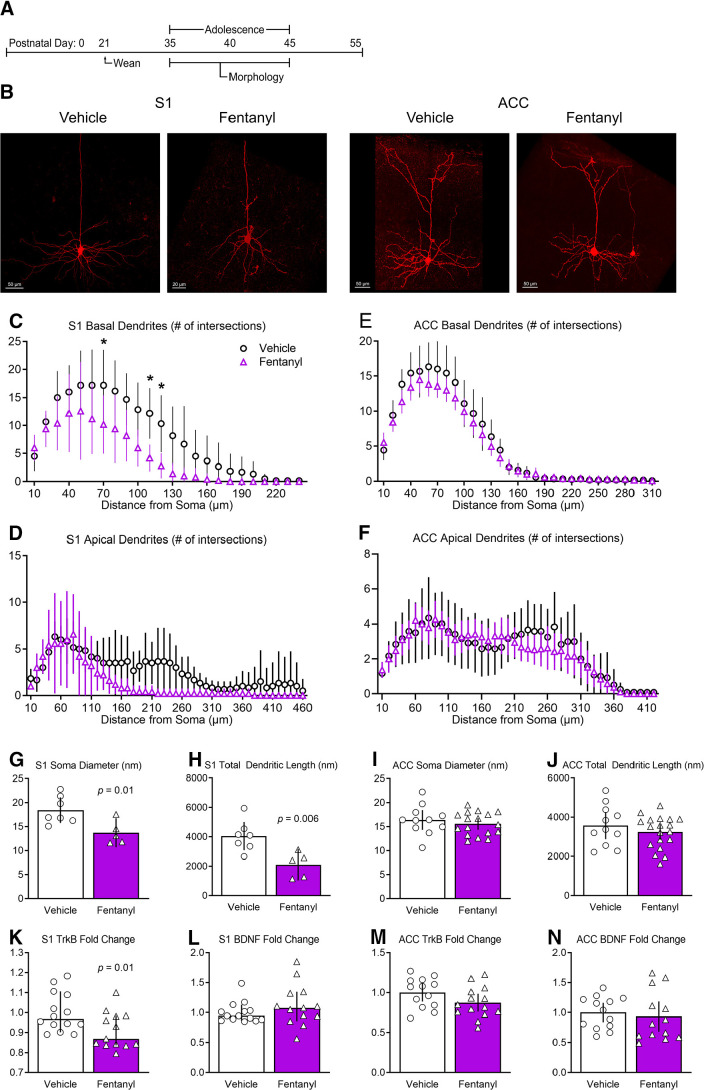
Figure 6.
Perinatal fentanyl exposure reduces morphology of basal dendrites of pyramidal neurons in S1. A, Timeline depicting morphologic assays of pyramidal neurons. B, Example of biocytin-filled layer 5 pyramidal neurons in S1 and ACC. Sholl analysis reveals that perinatal fentanyl exposure results in reduced branching of S1 basal (C) but not apical dendrites (D). There were no differences in branching of ACC basal (E) or apical dendrites (F). Fentanyl-exposed mice exhibited, in S1, decreased soma diameter (G) and decreased total dendritic length (H). Fentanyl-exposed mice also had decreased mRNA expression of TrkB receptors (K), with no difference in expression of BDNF (L). In ACC, there were no differences in soma diameter (I), total dendritic length (J), mRNA expression of TrkB receptors (M), or BDNF (N). Data depict means for parametric or medians for non-parametric comparisons with 95% confidence intervals. *p < 0.05.