FIGURE 1.
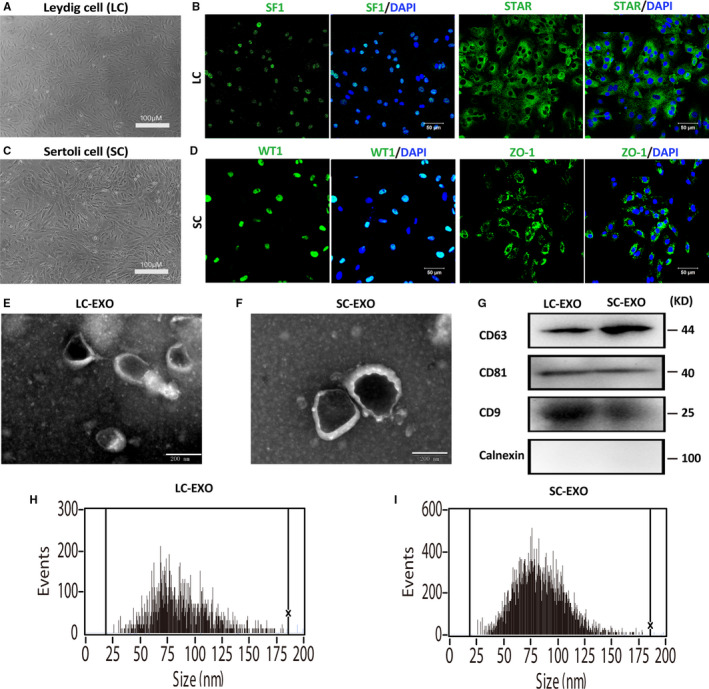
Characterization of SC‐derived exosomes (SC‐EXO) and LC‐derived exosomes (LC‐EXO). A, Representative images of cultured Leydig cells morphology. B, Detection of markers in Leydig cell. The cultured Leydig cells were positive for SF‐1 and StAR. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 100 μm. C, Representative images of cultured Sertoli cells morphology. D, Detection of markers in Sertoli cells. The cultured Leydig cells were positive for WT1 and ZO‐1. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 100 μm. E‐F, Exosomes released by Leydig cells (LC‐EXO) and Sertoli cells (SC‐EXO) were detected by electron microscopy. Scale bars, 200 nm. G, The presence of exosomal marker proteins, including CD63, CD9 and CD81, was confirmed by Western blots in SC‐EXO and LC‐EXO. Calnexin was used as negative control. H‐I, Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) demonstrates the size distribution of LC‐EXO and SC‐EXO
