Figure 4.
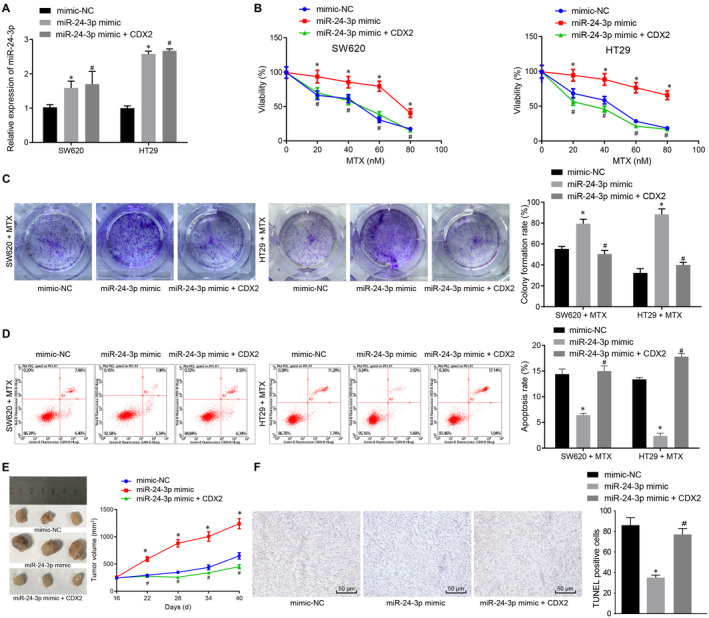
miR‐24‐3p enhances MTX resistance in CC via CDX2 down‐regulation. SW620 and HT29 cells were transfected with mimic NC, miR‐24‐3p mimic or miR‐24‐3p mimic + CDX2, followed by MTX treatment. A, The expression of miR‐24‐3p in SW620 and HT29 cells determined by RT‐qPCR normalized to U6. B, Cell viability of transfected SW620 and HT29 cells after 5 d of MTX treatment detected by CCK‐8 assay. C, Colony formation assessed by colony formation assay. D, Flow cytometry analysis of transfected SW620 and HT29 cell apoptosis. Mice were transfected with mimic NC, miR‐24‐3p mimic or miR‐24‐3p mimic + CDX2, followed by MTX treatment. E, Microscopic observation of tumour size and tumour volume (n = 10). F, TUNEL staining of apoptosis in tumour tissues (n = 10; ×200). * P < .05 vs cells or mice treated with mimic NC + MTX. # P < .05 vs cells or mice treated with miR‐24‐3p mimic + MTX. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Comparisons among multiple groups were conducted by one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Data at different time‐points were compared by repeated‐measures ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test
