Fig. 1. δ-Secretase cleaves UNC5C at N467 and N547 residues in vitro.
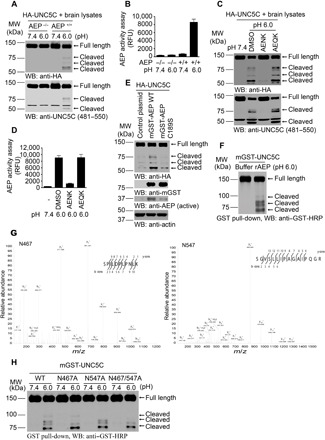
(A and B) HA-UNC5C was incubated with brain lysates derived from WT (AEP+/+) or AEP KO (AEP−/−) mice at pH 7.4 or 6.0, respectively. Western blot (WB) showed that UNC5C was cleaved at pH 6.0 by AEP+/+ brain lysates when AEP was activated. (B; means ± SEM; n = 3). (C and D) The proteolysis of UNC5C is blocked by Fmoc-Ala-Glu-Asn-Lys-NH2 (AENK) peptide, but not by Fmoc-Ala-Glu-Gln-Lys-NH2 (AEQK). δ-Secretase activity was inhibited by AENK (D; means ± SEM; n = 3). (E) Mutant of δ-secretase C189 diminishes UNC5C cleavage. HEK293 cells cotransfected with HA-UNC5C and mGST-AEP WT, mGST-AEP C189S, or control plasmid were incubated in buffer (pH 6.0) at 37°C for 45 min. (F) WB showed the processing of purified GST-UNC5C by recombinant δ-secretase (rAEP). (G) Mass spectrometry analysis of recombinant UNC5C fragmented by δ-secretase. The detected peptide sequences indicated that N467 and N547 were the two main cleavage sites. The detected peptides of UNC5C are 468–478 and 548–563, respectively. The sequences are shown in the upper right of each image. (H) Cleavage of mutant UNC5C by rAEP. UNC5C cleavage was analyzed by WB after GST–UNC5C WT, N467A, N547A, or N467A/N547A mutant was incubated with rAEP.
