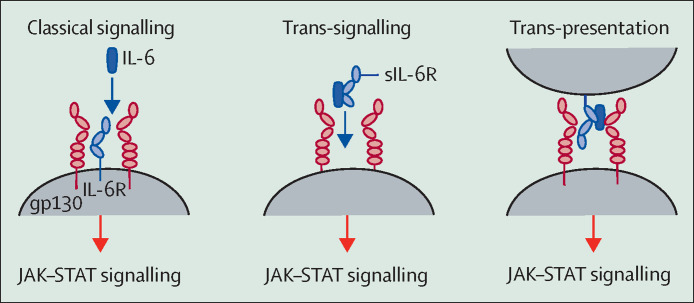
Figure 2.
The different types of IL-6 signalling
In classical signalling, IL-6 binds the membrane-bound IL-6R to form an IL-6–IL-6R complex, which subsequently associates with gp130 to generate signal transduction via the JAK–STAT pathway. IL-6 can also bind to soluble forms of the IL-6R before converging on gp130 (trans-signalling), or be trans-presented from dendritic cells via their membrane-bound IL-6R to T cells (trans-presentation). In general terms, classical signalling causes the physiological, anti-inflammatory, and pro-resolution effects of IL-6, with the pathological effects of the cytokine mediated by trans-signalling and trans-presentation. Importantly, monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R, such as tocilizumab, do not discriminate between these signalling types, and instead block all IL-6 signalling. gp130=glycoprotein 130. IL-6=interleukin-6. IL-6R=interleukin-6 receptor. JAK=Janus kinase. sIL-6R=soluble interleukin-6 receptor. STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription.