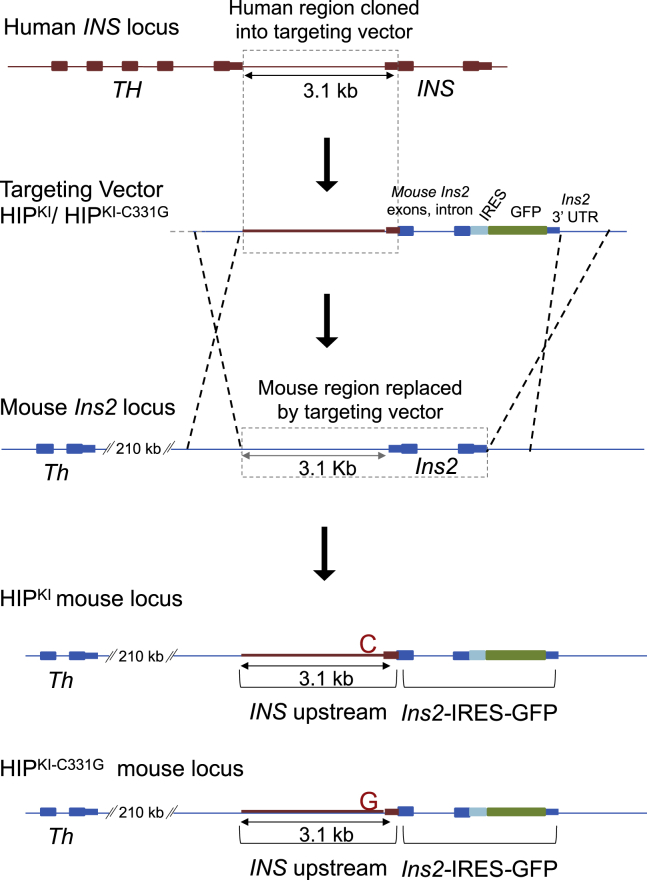
Figure 2.
Generation of HIPKI and HIPKI-C331G mouse alleles
A rectangle with dotted lines in the top two panels depicts the 3.1-kb human sequence located between the human TH and INS genes (including INS 5′ untranslated transcribed sequences), which was cloned into a targeting vector. This targeting vector contained the 3.1-kb human INS upstream region followed by Ins2-IRES-GFP, which includes mouse Ins2 exons and intron and an IRES, GFP, and Ins2 3′ UTR and was flanked by mouse Ins2 homology arms. Targeted replacement of the indicated mouse Ins2 sequence with this human upstream INS sequence followed by Ins2-IRES-GFP was carried out by homologous recombination. The same process was used to create two allelic versions carrying the normal human INS sequence or the c.-331C > G mutation. A neomycin cassette flanked by LoxP sites was excised in vivo and is omitted for simplicity. The sequence of the neomycin-excised targeted allele is provided in File S1.