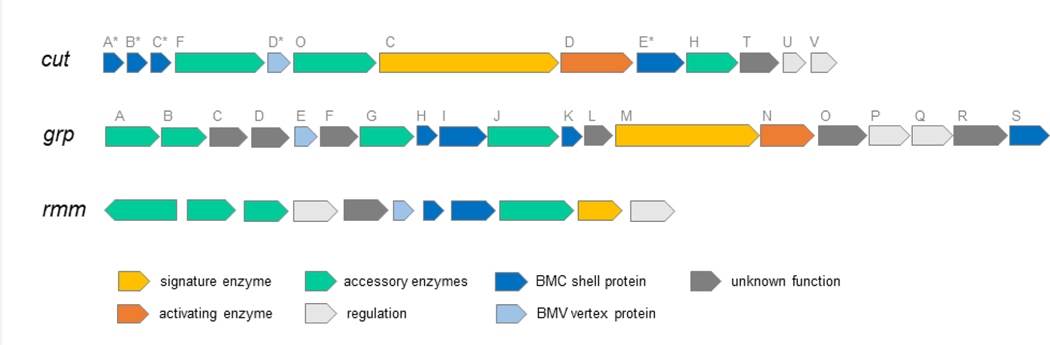
Figure 2: Operon layouts for several new classes of MCPs.
cut: choline utilization genes of E. coli 536 [5]. Asterisks on shell proteins designate different nomenclature; these genes are designated (choline microcompartment) cmcA-E rather than cut. grp: glycyl radical-propanediol genes from E. coli CFT073 [20]. rmm: Rhodococcus and Mycobacterium MCP from Mycobacteria smegmatis MC2 [25]. In general, MCPs are encoded by large operons that are sufficient for MCP formation. Signature enzymes are pathway specific enzymes characteristic of the metabolite processed by a particular MCP. Activating enzymes are Fe-S cluster dependent radical-SAM (S-adenosylmethionine) enzymes required to initiate glycyl radical formation in glycyl radical enzymes.