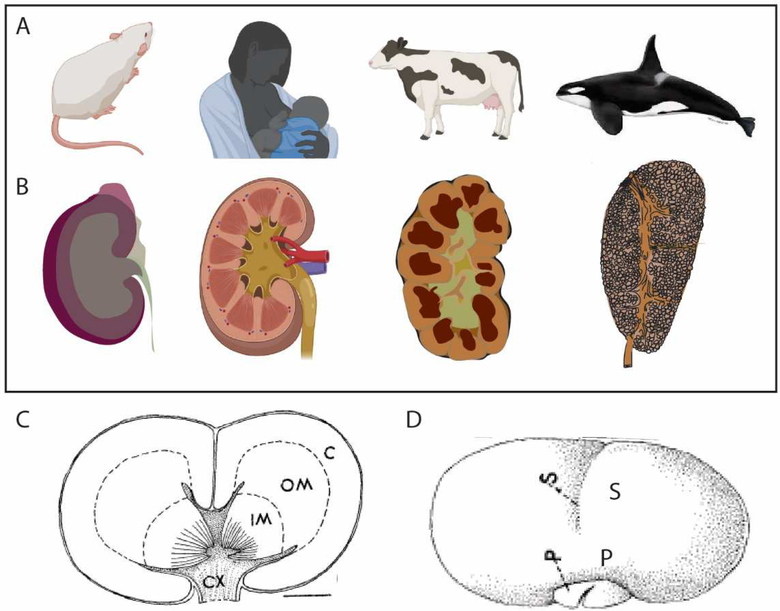
Figure 6. Reniculism as an approach to creating more renal mass.
A. Mammal model. B. Structure of the adult kidney. The mouse kidney (length 1cm, mass 400mg) is a single lobe with a single papilla. While the human kidney (10–13cm, 110g) contains multiple lobes and papillae, the organ has a fusiform nature with a smooth outer capsule. The bovine kidney is multilobular with persistent separation between lobes with lobes arranged in a single layer. The kidney of the killer whale (>25cm, 4.5kg) is comprised of >1000 individual renicules each with one (82%) or two (18%) papillae that are arranged in up to 8 layers with individual renicules surrounded by separating connecting tissue. All renicules drain into a united ureteric tree for exit via a single ureter. C. Diagram of a longitudinal cross section of a single killer whale reniculate showing dual papillae. C, cortex; OM, outer medulla, IM, inner medulla, CX, calyx. Scale bar = 2.1 mm. D. External view of a single killer whale (Orcinus orca) renicule. Note that not all sulci represent separate lobes. P, papilla, S, sulcus. Killer whale data adapted from [125].