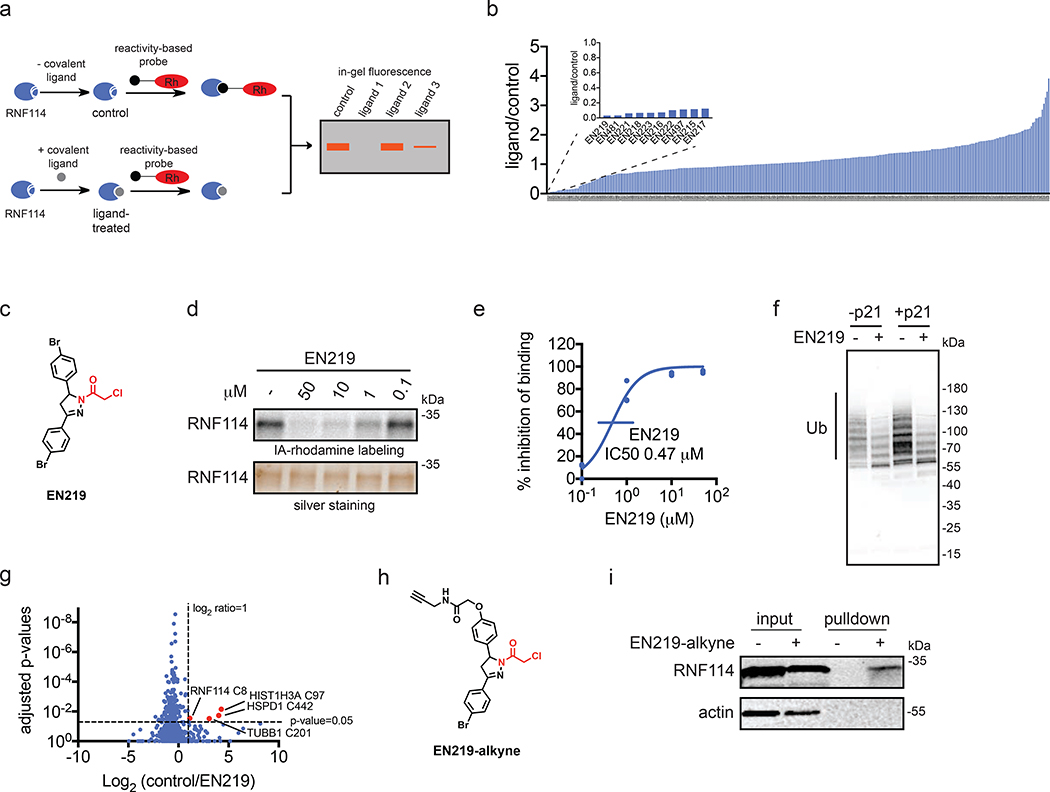
Figure 2. Covalent ligand screening against RNF114.
(a) Gel-based ABPP assay for screening covalent ligands against IA-rhodamine probe binding to pure RNF114 protein. Loss of fluorescence indicates covalent ligand binding to a cysteine on RNF114. (b) Quantified results from gel-based ABPP screen of 318 cysteine-reactive acrylamides and chloroacetamides against IA-rhodamine labeling of RNF114. DMSO vehicle or covalent ligands (50 μM) were pre-incubated with pure RNF114 protein (0.1 μg) for 30 min prior to addition of IA-rhodamine (100 nM) for 30 min at room temperature. Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and in-gel fluorescence was quantified. Raw gel-based ABPP data shown in Figure S1. 1. Structures of compounds screened can be found in Table S1. Data expressed as ligand/control ratio of in-gel fluorescent intensity. Shown in the inlay are the ligand/control ratios for the top 10 hits. (c) Structure of top hit EN219 with chloroacetamide cysteine-reactive warhead in red. (d) Dose-response of EN219 interaction with RNF114 by competitive gel-based ABPP. DMSO vehicle or covalent ligands were pre-incubated with pure RNF114 protein (0.1 μg) for 30 min prior to addition of IA-rhodamine (100 nM) for 30 min at room temperature. Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and in-gel fluorescence was quantified. Gels were also silver-stained as a loading control. (e) Percent inhibition of IA-rhodamine binding to RNF114 in (d) was quantified and 50 % inhibitory concentration (IC50) was determined to be 0.47 μM. (f) RNF114-mediated autoubiquitination and p21 ubiquitination in vitro. DMSO vehicle or EN219 (50 μM) was incubated with pure RNF114 for 30 min prior to addition of PBS or p21, ATP, and FLAG-ubiquitin (Ub) for 60 min. Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and blotted for FLAG. Ubiquitinated-RNF114/p21 is noted. (g) IsoTOP-ABPP analysis of EN219 in 231MFP breast cancer cells. 231MFP cells were treated in situ with DMSO vehicle or EN219 (1 μM) for 90 min. Control and treated cell lysates were labeled with IA-alkyne (100 μM) for 1 h, after which isotopically light (control) or heavy (EN219-treated) biotin-azide bearing a TEV tag was appended by CuAAC. Proteomes were mixed in a 1:1 ratio, probe-labeled proteins were enriched with avidin and digested with trypsin, and probe-modified peptides were eluted by TEV protease and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Average light-to-heavy (control/EN219) ratios and adjusted p-values were quantified for probe-modified peptides that were present in two out of three biological replicates and plotted. Shown in red are protein and modified cysteine site for peptides that showed >2-fold control/EN219 ratio with adjusted p-value <0.05. Full data can be found in Table S2. (h) Structure of alkyne-functionalized EN219 probe. (i) EN219-alkyne pulldown of RNF114. 231MFP cells were treated with DMSO vehicle or EN219-alkyne (50 μM) for 90 min. Biotin-azide was appended to probe-labeled proteins by CuAAC and probe-labeled proteins were avidin enriched and blotted for RNF114 and negative control actin. An aliquot of input proteome from vehicle-and EN219-treated cell lysates was also subjected to blotting as an input control. Data shown in (e) are average values and individual replicate values. Data shown are from n=1 in (b) and n=3 for (d-f, i) biological replicate(s) per group. Gels shown in (d, i) are representative gels from n=3 biological replicates per group. This figure is related to Figures S1–2.