Figure 7: Myofiber stiffening by CARP.
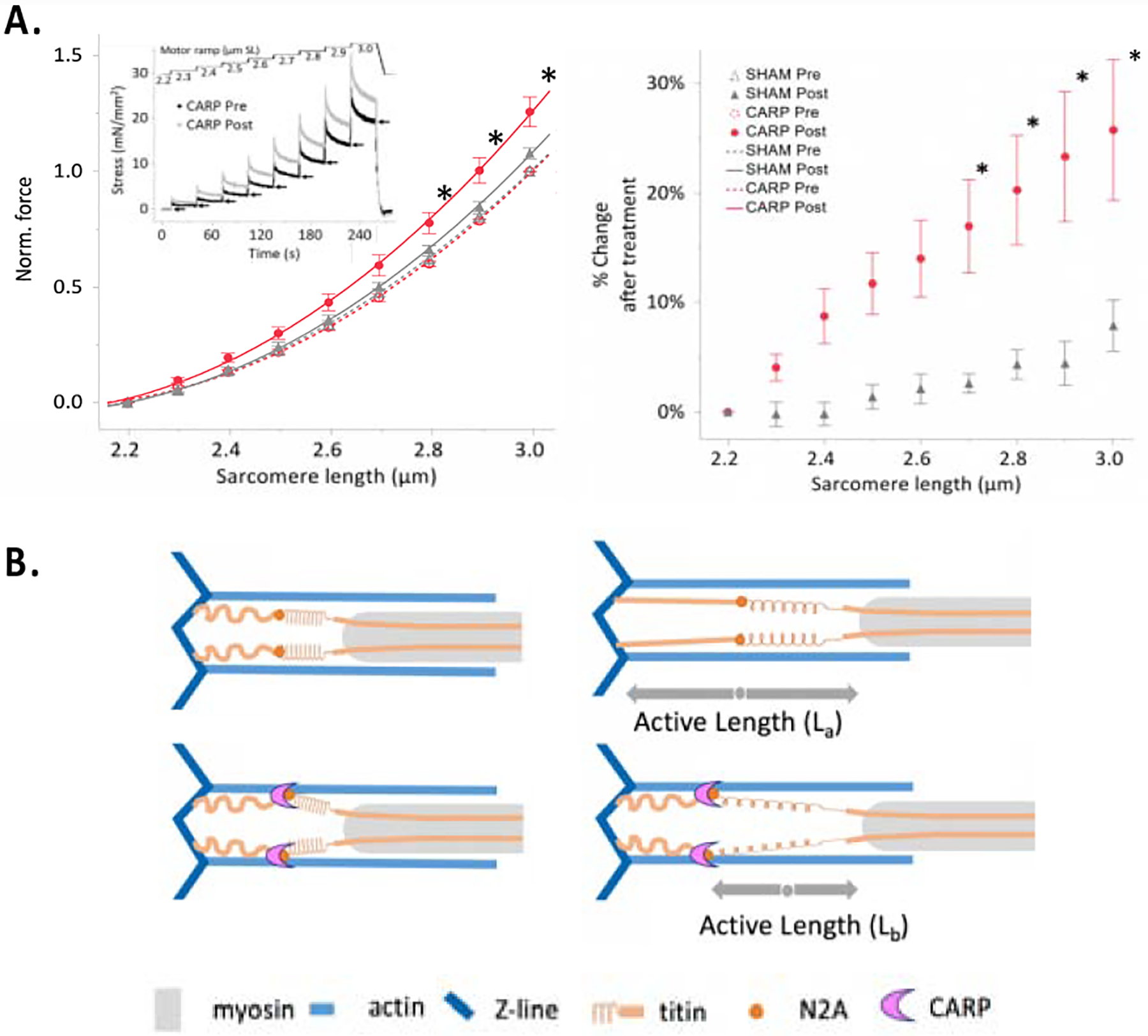
A. Passive force of permeabilised fiber bundles. (Left) The passive force-SL curves from fibers pre- and post-treatment with CARP (n = 10) or sham (n = 9) proteins. Data are fitted with second order polynomials (R2 > 0.92) and surrounded by the 95% confidence interval of the fit. Inset, mechanics protocol. Arrows indicate quasi-steady-state forces that were used to calculate data points in main figure. (Right) The percent change in force after treatment of CARP or the sham protein mCitrine, relative to before treatment. *P < 0.01, CARP treated vs all else (mean ± s.e.m); B. Proposed mechanical role of a potential CARP-based clamp. The CARP-mediated cross-linking of titin and actin at the N2A locus might effectively incapacitate the extension of titin’s proximal spring, enhancing the contribution of the stiffer PEVK region. Thereby, CARP could cause titin isoforms to perform as shorter, stiffer variants.
