Figure 7. Molecular modeling of changes in the α1 sGC catalytic domain induced by Cys517→Tyr substitution.
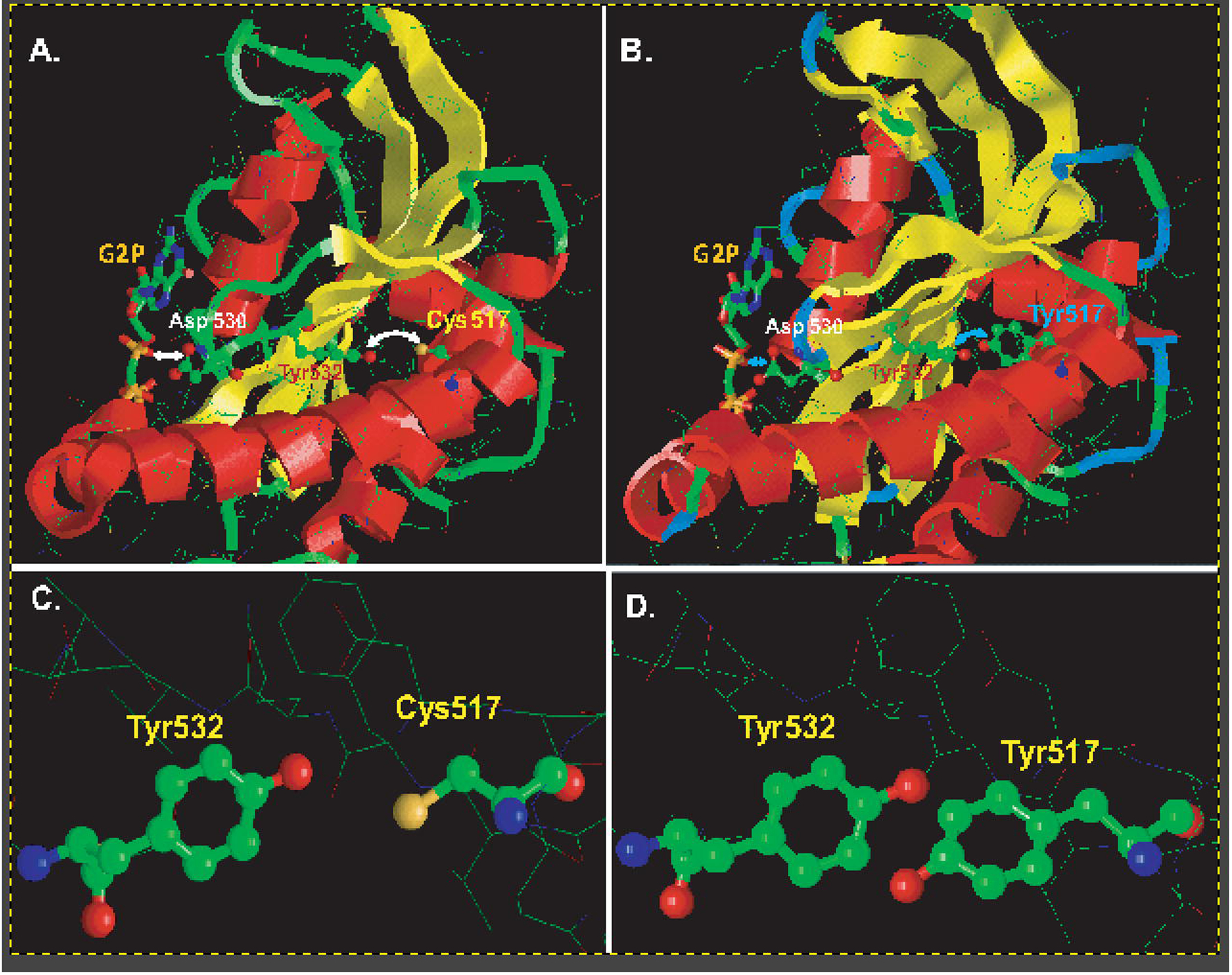
(A): Close up view of the α1 catalytic region of wild type sGC based on the cryo-EM structure of NO-stimulated human sGC (PDB 6JT2). The residues Cys517, Tyr532, Asp530 and the GTP analog are highlighted. (B): Close up view of the α1 catalytic region of the α1Cys517Tyrβ mutant. The model was generated using the SWISS-MODEL platform based on PDB 6JT2. The residues Tyr517, Tyr532, Asp530 and the GTP analog G2P (phosphomethylphosphonic acid guanylate ester) are highlighted. For simplicity of viewing, the catalytic region of the β1 subunit is omitted in both (A) and (B). The arrows highlight the cross-talk between residue 517 and Tyr532 and the associated distance between residues Asp530 and the GTP substrate analog. (C-D): Close up view of residues 517 and Tyr532 shows that in wild type sGC (C) Cys517 and Tyr 532 are more remote than the juxtaposed Tyr517 and Tyr532 in α1Cys517Tyrβ mutant (D).
