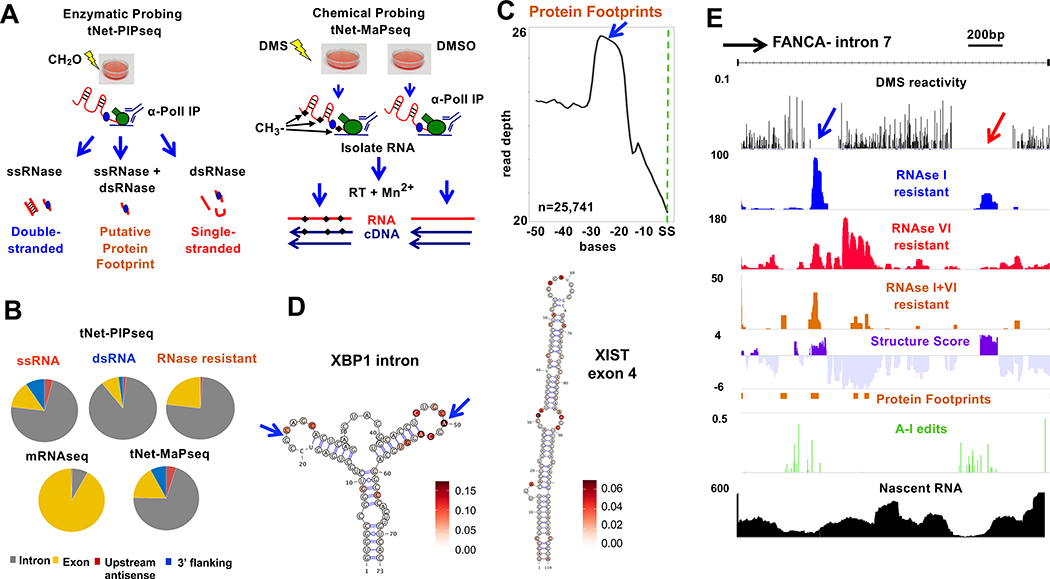
Figure 1. tNET-Structureseq mapping of nascent RNA structure.
A. Enzymatic (tNet-RNAse-seq ) and DMS (tNet-MaPseq ) probing of nascent pol II transcripts.
B. Distribution of tNet-RNAse-seq and tNet-MaPseq compared to mRNAseq reads in HEK293 WT Amr pol II cells.
C. Metaplot of putative exon junction complex footprints (RNAse I+VI resistant, blue arrow) upstream of splice sites (SS).
D. Predicted structures with DMS reactivities of the non-canonical XBP1 intron (arrows) (Yoshida et al., 2001) (chr22:29,192,089–29,192,172) and XIST exon 4 (chrX :73,050,979–7,3051,093) within nascent RNA.
E. Nascent RNA structure across an intron (chr16:89,867,703–89,871,732). Normalized DMS reactivity, RNAse I, RNAse VI and RNAse I+VI resistant reads, fraction of A-I editing per base and nascent RNA seq reads (tNET-seq) are shown.