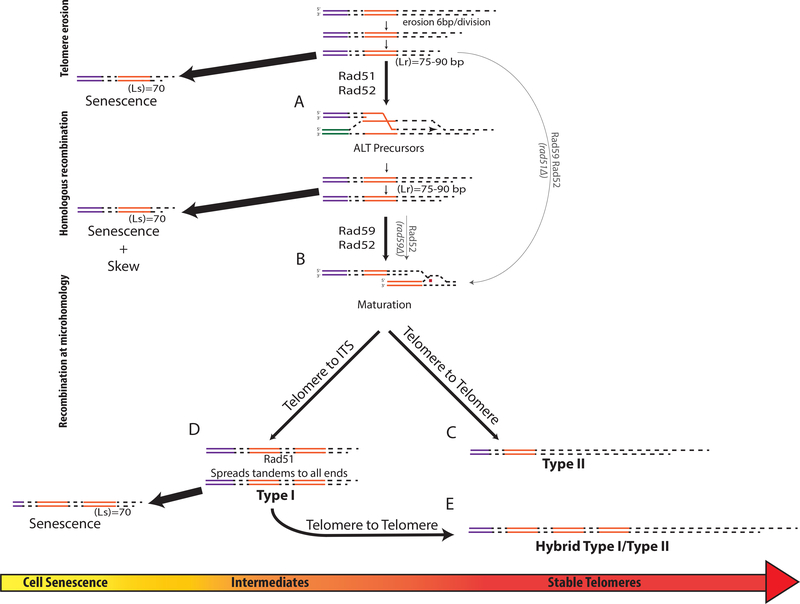
Figure 7. The model of the unified ALT pathway.
(A) Following inactivation of telomerase, the telomeres erode at a rate of 6bp/div. until Lr is reached (inducing HR) or Ls is reached (inducing senescence). Rad51, Rad52-dependent HR leading to telomere elongation forms ALT precursors.
(B) Rad59/Rad52 mediates the maturation of precursors, from (A), into ALT survivors by recombination at microhomologies. Thin lines: alternative pathways in the absence of Rad51 or Rad59.
(C) Rad59, Rad52 mediate recombination at microhomologies within telomeres to form Type II survivors.
(D) Rad59, Rad52 mediate recombination between eroded telomere and ITS to form tandem Y’ that are propagated to other chromosomal ends through Rad51-dependent recombination.
(E) Rad59, Rad52 mediate maturation of products of (D) to form “hybrid” ALT outcomes containing long telomeres.