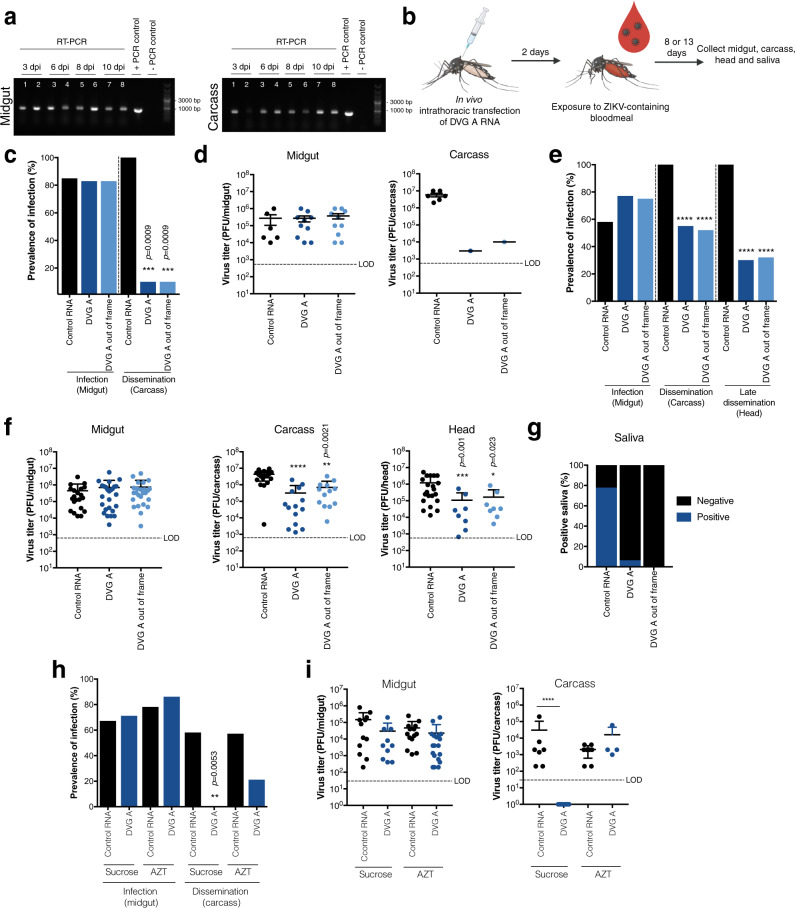
Fig. 6. Zika virus DVG inhibits virus dissemination and blocks transmission in experimentally-infected mosquitoes.
a Longevity of DVG-A in mosquitoes. Ae. aegypti mosquitoes were in vivo transfected with equimolar solutions of DVG-A or DVG-A out-of-frame RNA. At the indicated times post transfection, 5 mosquitoes were salivated and midgut, carcass, and head dissected. RNA was extracted from homogenates of a pool of the 5 mosquitoes and RT-PCR specific for the DVG was performed. Results from a representative experiment out of two is shown. Lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7 = DVG-A out-of-frame, Lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8 = DVG-A. Results for head and saliva samples are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11a. b Schematic representation of the experimental design. Ae. aegypti mosquitoes were injected with a transfection mix 0.02 pmoles of RNA. 2 days post-transfection, mosquitoes were fed a bloodmeal containing 2x106 PFU/mL of Zika virus, and dissected at 8 or 13 d p.i. c Prevalence of Zika virus infection in the midgut or carcass of mosquitoes pre-transfected with control (n = 7), DVG-A (n = 12) or DVG-A out-of-frame (n = 12) RNA 8 d p.i. ***p = 0.0009 (by Fisher’s exact test, two-sided). d Viral load in infected mosquitoes from the midgut (control: n = 6; DVG-A: n = 10; DVG-A out-of-frame: n = 10) or carcass (control: n = 6; DVG-A: n = 1; DVG-A out-of-frame: n = 1) of the mosquitoes from (c). Mean and SD are shown. For midgut data, a one-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s multiple comparison was performed. For carcass, no statistical test was performed because due to n = 1. e Prevalence of Zika virus infection in the midgut, carcass or heads of mosquitoes pre-transfected with control (n = 36), DVG-A (n = 35) or DVG-A out-of-frame (n = 33) RNA 13 d p.i. ****p ≤ 0.0001 (by Fisher’s exact test, two-sided). f Viral load in the organs of the same infected mosquitoes from (e): midgut (control: n = 21; DVG-A: n = 26; DVG-A out-of-frame: n = 25), carcass (control: n = 21; DVG-A: n = 13; DVG-A out-of-frame: n = 13), or heads (control: n = 21; DVG-A: n = 8; DVG-A out-of-frame: n = 8). Mean and SD are shown. ****p ≤ 0.0001 (by one-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s multiple comparison). g Percentage Zika virus-positive saliva in mosquitoes pre-transfected with control (n = 9), DVG-A (n = 16) or DVG-A out-of-frame (n = 13) RNA 13 d p.i. h Prevalence of Zika virus infection in the midgut or carcass of sucrose- or AZT-fed mosquitoes that were injected with control or DVG-A RNA. Prevalence was assessed at 7 d p.i. Control RNA, sucrose fed (n = 18); DVG-A RNA, sucrose fed (n = 14); control RNA, AZT fed (n = 18); DVG-A RNA, AZT fed (n = 22). **p = 0.0053 (by Fisher’s exact test, two-sided). i Viral load in the midgut (control, sucrose fed: n = 12; DVG-A, sucrose fed: n = 10; control, AZT fed: n = 14; DVG-A, sucrose fed: n = 19) or carcass (control: n = 7; DVG-A: n = 10<LOD; control, AZT fed: n = 8; DVG-A, sucrose fed: n = 4) of the same mosquitoes from (h). Mean and SD are shown. ****p ≤ 0.0001 (by one-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s multiple comparison). Data from two independent experiments is shown. LOD = limit of detection. Control RNA: pTRI-Xef RNA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.