Fig. 3. Computational prediction of the binding affinity of gefitinib toward EGFR-WT, L858R, and L747P mutants.
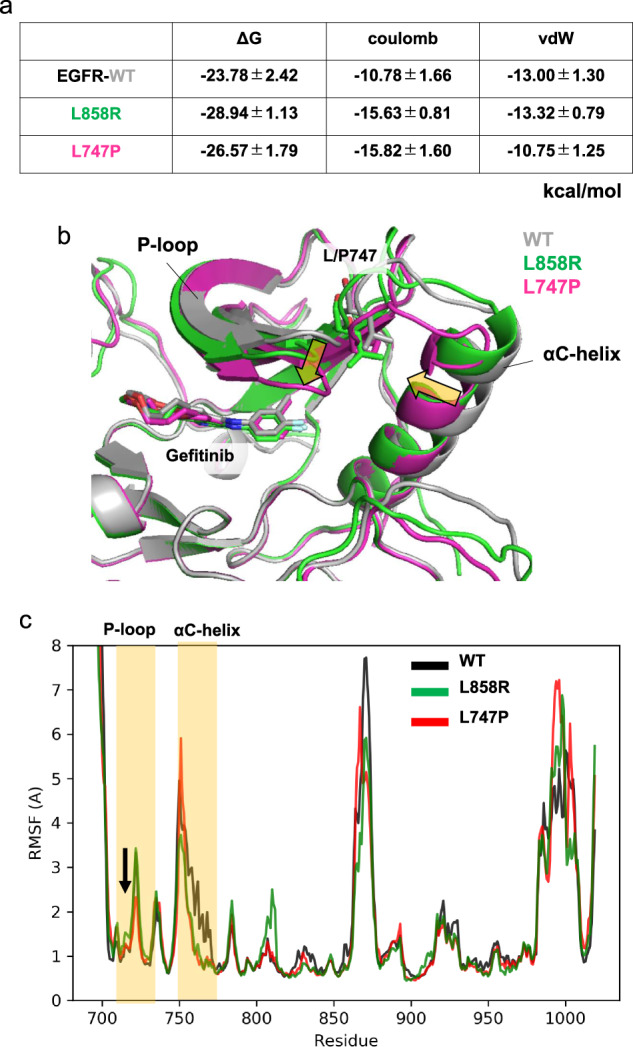
a Binding free energies (ΔG) of gefitinib toward EGFR-WT, L858R, and L747P mutants. Electrostatic (Coulomb) and van der Waals (vdW) contributions to the ΔG values are also indicated. The binding affinity for the L747P mutant is significantly lower than that for the L858R mutant owing to the loss of vdW interactions. b The mean structures of 1 μs × 3 MD simulations. The protein backbone is represented by a ribbon diagram, and gefitinib and L/P747 are depicted as sticks (C, gray/green/magenta; N, blue; O, red; F, cyan). Orientational changes in the phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) and αC-helix upon the L747P mutation are indicated by yellow arrows. c Root‐mean‐square fluctuation (RMSF) of the backbone Ca atoms. RMSF values were calculated using MD trajectories of 1 μs × 3. P-loop and αC-helix regions are highlighted in yellow. Conformational flexibility of the P-loop in the L747P mutant is lower than that in WT or the L858R mutant, as indicated by an arrow.
