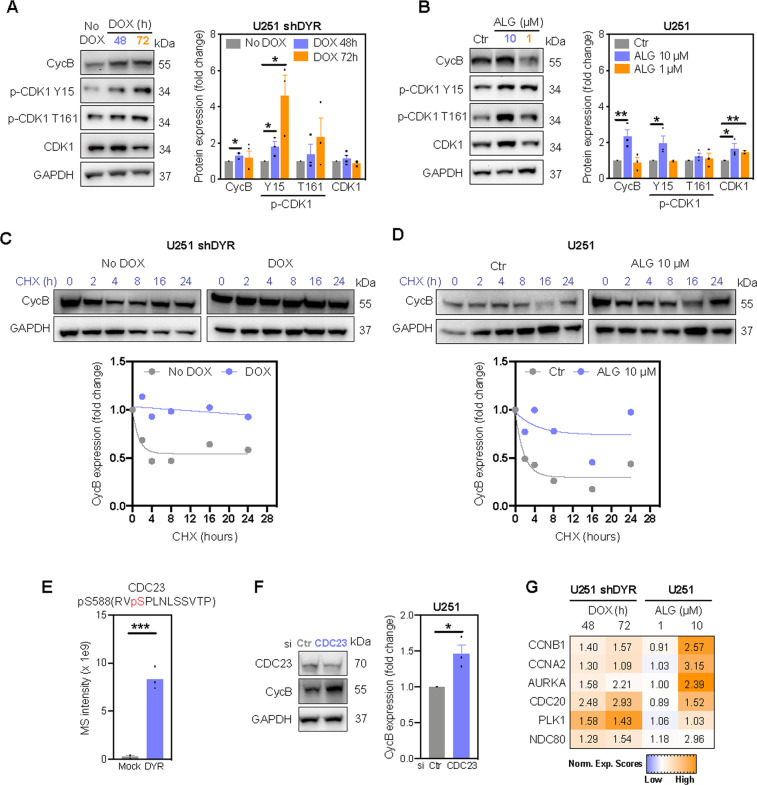
Fig. 3. DYRK1A inhibition prevents cyclin B degradation.
Immunoblot analysis and densitometric quantification of cyclin B (CycB), phosphorylated (p-CDK1) and total CDK1 in (A) U251 shDYR cells treated ± DOX and (B) U251 cells treated ± DYRK1A inhibitor ALGERNON (ALG, 72 h). Degradation of cyclin B (CycB) in U251 shDYR cells treated ± DOX (C) and U251 cells treated ± ALG (D). Cells were treated with DOX or ALG for 72 h before cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. Representative images and quantification from two independent experiments are shown. E Mass spectrometry (MS) intensity of CDC23 phosphorylated at S588 by DYRK1A in vitro. F Immunoblot analysis and densitometric quantification of cyclin B expression in cells transfected with siRNA targeting CDC23 (72 h). G Heatmap of protein levels of anaphase-promoting complex substrates cyclin B1 (CCNB1), cyclin A2 (CCNA2), Aurora kinase A (AURKA), cell-division cycle protein 20 (CDC20), Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and kinetochore protein NDC80 in U251 cells following doxycycline-induced DYRK1A knockdown (DOX) and inhibition with ALG (72 h). Data represent fold change of replicates to their respective controls. All bar graphs represent mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments (two-tailed unpaired t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).