Fig. 1. Protein translated from CVnCoV is cleaved, post-translationally modified and presented on the cell surface.
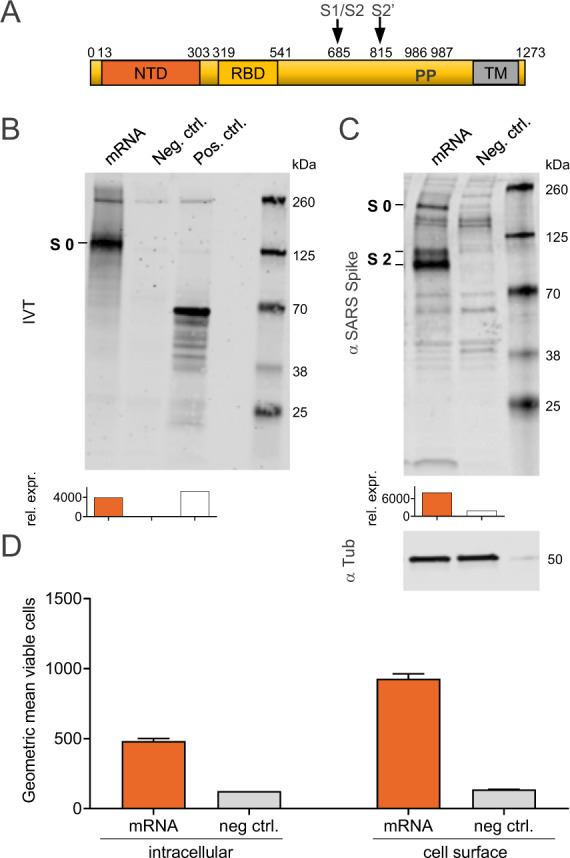
A Schematic drawing of SARS-CoV-2 S-2P encoded by CVnCoV. B In vitro translation of the mRNA component of CVnCoV in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate system. Translation of nascent proteins was detected via western blotting. Water and luciferase control mRNA were employed as negative and positive controls, respectively. HeLa cells were transfected with 2 µg of the mRNA component of CVnCoV. Twenty-four hours post transfection, cells were analysed for S expression via C western blotting using an S-specific antibody and D flow cytometric analyses using an S-specific antibody either with or without membrane permeabilisation allowing detection of total (intracellular) or cell-surface bound (cell surface) S protein. Relative protein expression in western blotting was quantified using the Image Studio Lite Ver 5.2 software. Geometric mean fluorescence intensity (GMFI) of transfected HeLa cells are expressed as mean + standard deviation (SD) of duplicate samples. Blots shown in C derive from the same experiment and were processed in parallel. NTD N-terminal domain, RBD receptor-binding domain, IVT in vitro translation, TM transmembrane domain, Tub Tubulin.
