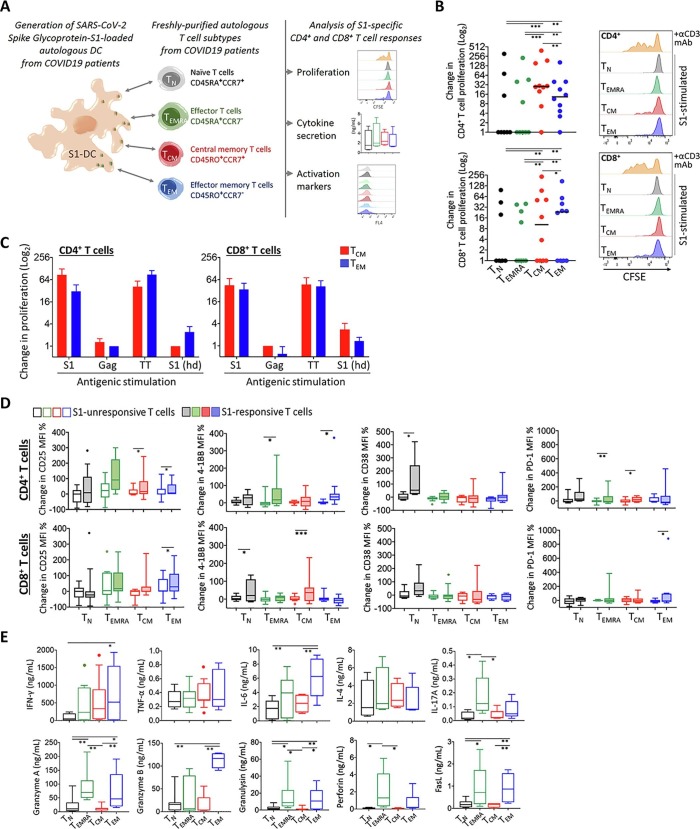
Fig. 1.
Assessment of functional responses in T cells from COVID-19 survivors. A) Graphical outline of the experimental setup is shown. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells were generated from the individuals with COVID-19 history and loaded with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein-S1 (S1-DC); then, autologous naïve T (TN), terminally-differentiated effector T (TEMRA), central memory T (TCM), and effector memory T (TEM) cells were purified and co-cultured with these DCs. T cell proliferation, expression of activation markers and cytokine secretion were measured after 96 h incubation. B) Change in CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation was plotted for each patient in comparison to that obtained with control co-cultures with monocyte-derived DCs without specific antigen loading. Representative flow cytometry histograms are given on the right side. The co-cultures stimulated with an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody served as a technical positive control for T cell proliferation. C) The patient-derived TCM and TEM cells’ proliferation response against the S1-DC was compared with those obtained with the HIV Gag or with the tetanus toxoid (TT) antigen-loaded DCs. T cells and S1-DCs obtained from healthy individuals (S1(hd)) were also used as controls. D) Changes in CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation marker levels were shown in comparison to those obtained with control co-cultures with monocyte-derived DCs without specific antigen loading. E) Amount of T cell-associated cytokines secreted into the co-culture supernatants was assessed. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).