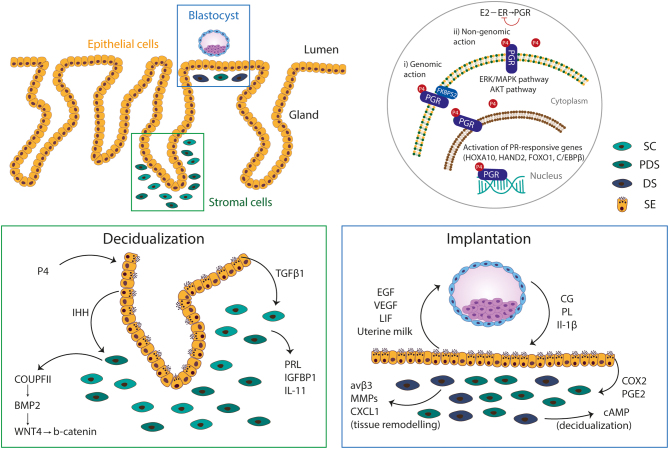
Figure 4.
Signalling pathways crucial for decidualization and implantation. Decidualization and implantation rely on continuous cellular interactions between epithelial cells at the surface and in glands, stromal cells and the incoming blastocyst (top left panel). Progesterone (PG) mediates its function through progesterone receptor (PGR) whose expression is induced by the action of oestrogen (E2) through oestrogen receptor (ESR1), and in turn, PGR inhibits ESR to create a negative feedback loop system. Upon binding of P4, PGR acts as a transcription factor which translocates to the nucleus to mediate genomic actions. Homeobox A10 (HOXA10), Forkhead Box O1 (FOXO1), heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2 (HAND2) and CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein-β (C/EBPβ) are transcription factors that are regulated by progesterone and are indispensable for decidualization. FK506 binding protein prolyl isomerase 4 (FKBP52) is a PGR chaperon that promotes the activity of the receptor during decidualization. PGR at the surface of the cells can also trigger downstream molecules to activate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK/MAPK) and Protein Kinase B (AKT) pathways and, thus, mediate non-genomic actions (top right panel). Progesterone activates the expression of Indian hedgehog (IHH) in the epithelium, a morphogen that promotes the decidualization of stromal cells via activation of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor II (COUPTFII) that subsequently regulates the expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2). BMP2 is a morphogen of the TGFB pathway, acting through Wingless 4 (WNT4). TGFB1 is another member of the TGFβ pathway secreted by epithelial cells. Subsequently, stromal cells are stimulated to produce prolactin (PRL), insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 (IGFBP1) and interleukin 11 (IL-11), classic markers of decidualization (bottom left panel). Upon attachment to the uterus, trophoblast secretes hormones, chorionic gonadotropin (CG) and placental lactogen (PL), as well as cytokines like interleukin 1β (IL1B). In turn, epithelial glands secrete uterine milk, a cocktail of glycoproteins (glycodelin-A, osteopontin, uteroglobin), glycogen, lipids, as well as, growth factors (leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). In addition, IL1B and CG reinforce decidualization by promoting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) and prostaglandin E synthase (PGE2) expression by epithelial cells and subsequently augmenting cAMP production from stromal cells. IL1β also acts on maternal stromal cells to promote expression of αvβ3 integrin, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10) which are necessary for tissue remodelling and angiogenesis to support trophoblast invasion (bottom right panel). SC, stromal cell; PDS, pre-decidualized stromal cell; DS, decidualized stromal cell; SE, secretory epithelial cell.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a