Table 2.
Transoesophageal echo assessment of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves.
| View (modality) | Explanatory notes | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Mid oesophageal 4-chamber at 0–15º (2D, CFM, CW, PW) | The septal and anterior/posterior leaflets of the TV are imaged in this view (see also Fig. 2 for explanation of imaging planes). Septal-lateral annular dimension can be measured at end-diastole. Note that CW assessment of TR jet velocity, and PW assessment of TV inflow should be attempted from multiple windows, according to the optimal alignment of the jet/s with the Doppler beam. |
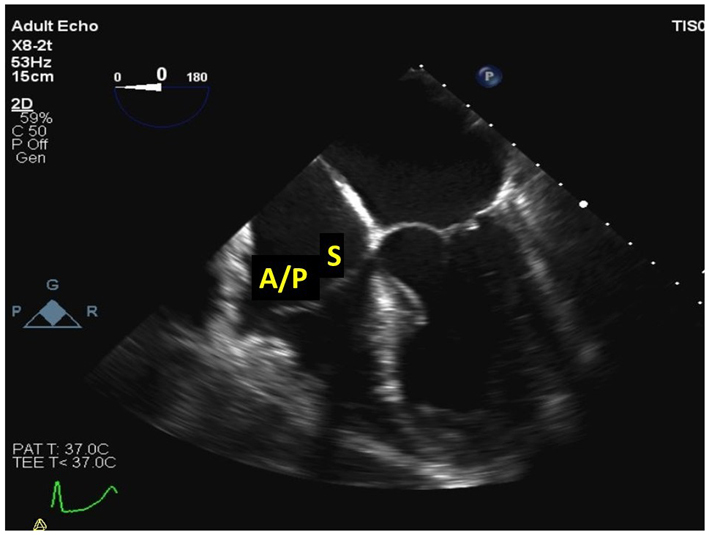 |
| Mid oesophageal 5-chamber view at 0–15º (2D, CFM, CW, PW) | Demonstrates the septal and anterior leaflets of the TV (see also Fig. 2 for explanation of imaging planes) | 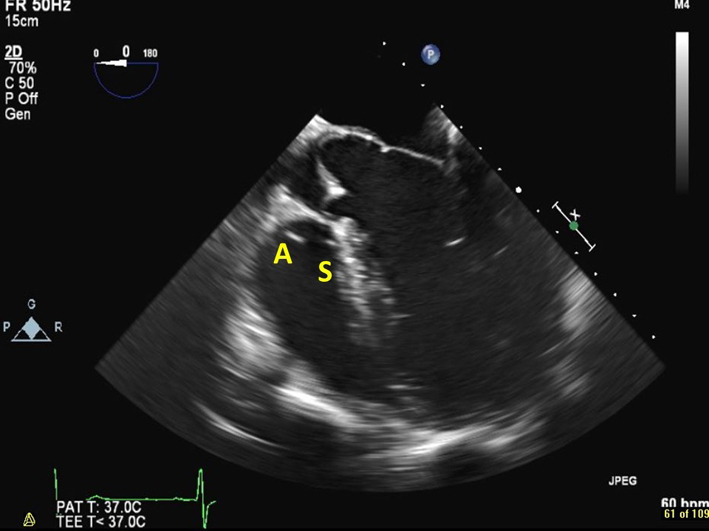 |
| Upper oesophageal at 0–15º (2D, CFM) | If the probe is withdrawn slightly from the mid oesophageal window, the main PA and PA bifurcation can be visualised. Doppler may demonstrate holodiastolic flow reversal in a branch PA in severe PR. | |
| Mid oesophageal, RV inflow-outflow view at 45–60º (2D, CFM, CW, PW) | Demonstrates the anterior or septal TV leaflets adjacent to the aortic valve, and the posterior leaflet laterally. The RVOT, PV and PA are also visualised in this view. | 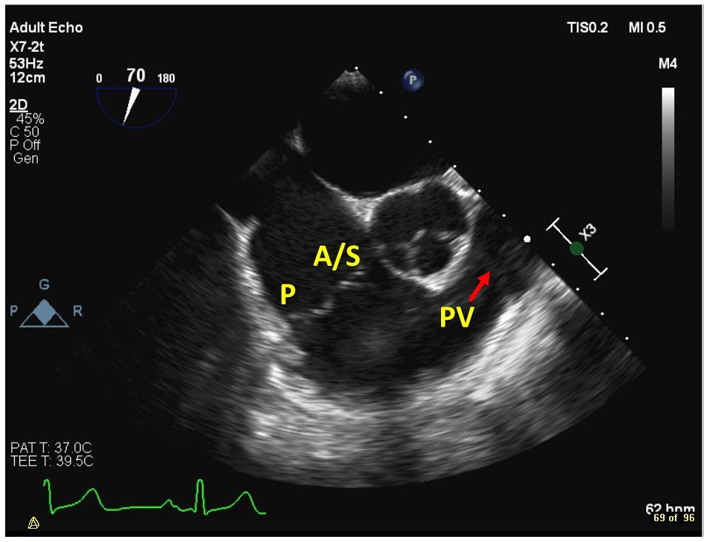 |
| Mid oesophageal, at 90º (2D, CFM) | The RVOT, PV and PA are well visualised in this view |  |
| Mid oesophageal modified bicaval view at 80–130º (2D, CFM, CW, PW) | Visualises the posterior and anterior leaflets of the TV. The TR jet is often well-aligned for CW Doppler assessment in this view. PW assessment of TV inflow is also often well-aligned from this view. The superior vena cava (SVC) is seen to the right of the image. The CS is denoted by the red star. | 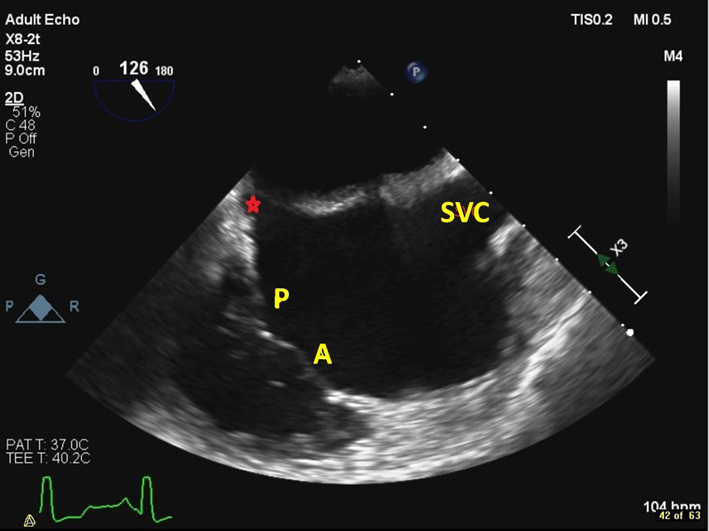 |
| Distal oesophageal, near the gastro-oesophageal junction at 0–15º (2D, 3D, CFM, CW, PW) | From this lower plane only the RA and coronary sinus lie directly in the beam of the probe. This view is therefore ideal for acquiring 3D volumes of the TV without interference from intervening left heart structures. The CS is denoted by the red star. | 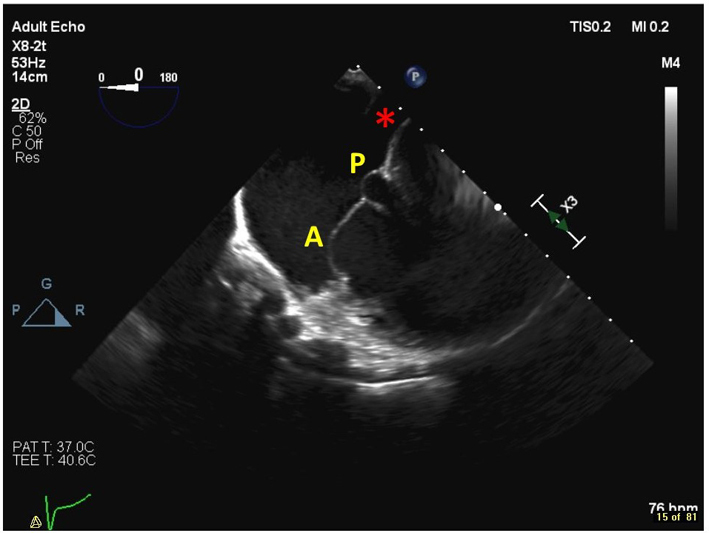 |
| Transgastric basal SAX view at 90º (2D, CFM) | This is the only 2D imaging plane in which all 3 tricuspid leaflets can be visualised simultaneously. The septal leaflet (S) is closest to the LV. The posterior leaflet (P) is in the near field, and the anterior leaflet (A) is in the far field. | 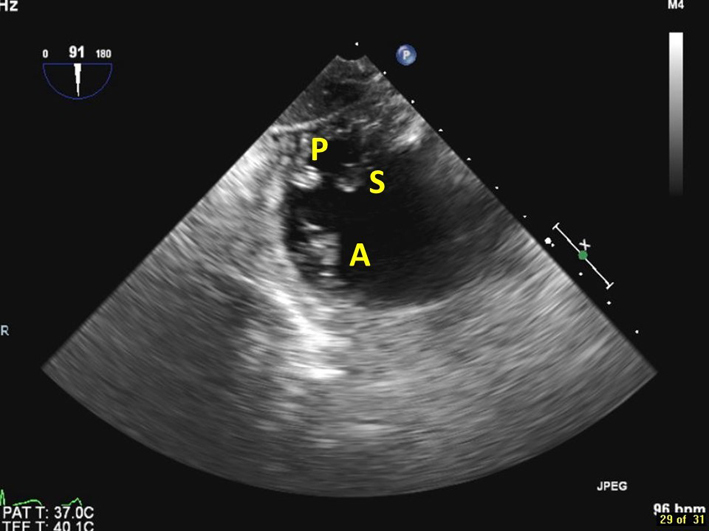 |
| Trangastric RV inflow view, at 80–120º (2D, CFM) | Images the anterior (ant) and inferior (inf) walls of the RV, as well as the papillary muscles, chordae, and TV. The posterior TV leaflet (P) is usually seen in the near field. | 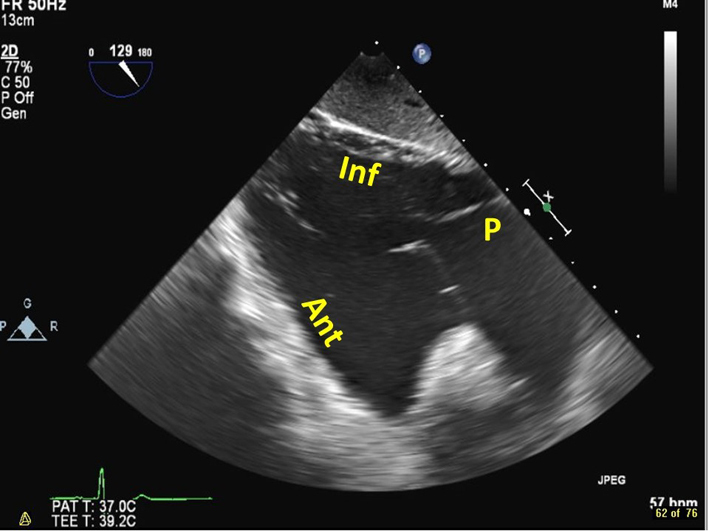 |
| Transgastric RV inflow-outflow view, at 100–120º (2D, CFM) | Images the RA, RV, RVOT and PA. The posterior TV leaflet (P) is usually seen in the near field, and the anterior leaflet (A) in the far field. | 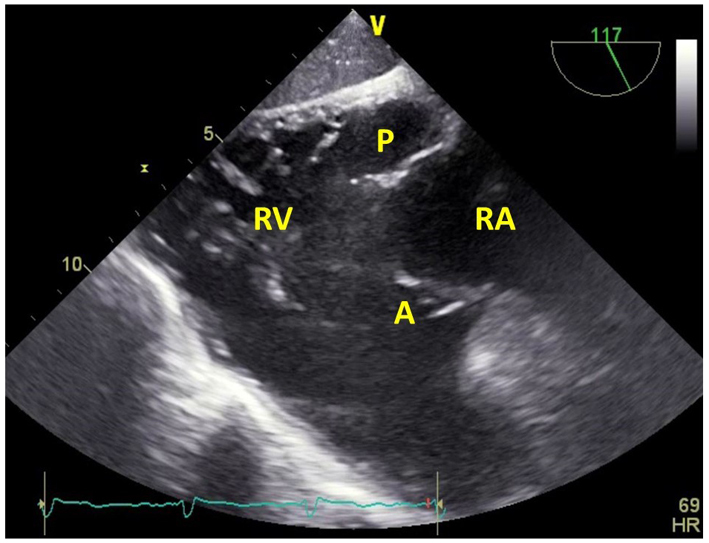 |
| Deep transgastric RV inflow-outflow view at 100–120º (2D, CFM, CW, PW) | The PV is also well visualised in the deep trangastric window at 120°. Doppler measurements through the PV may be well-aligned in this view. | 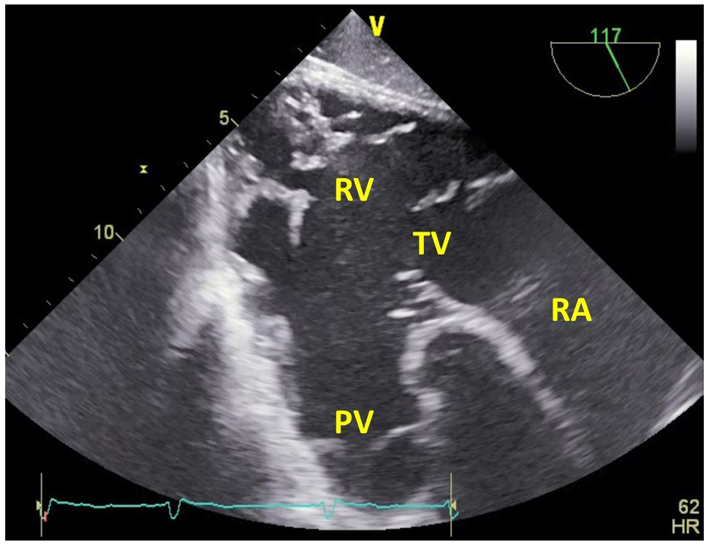 |

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a