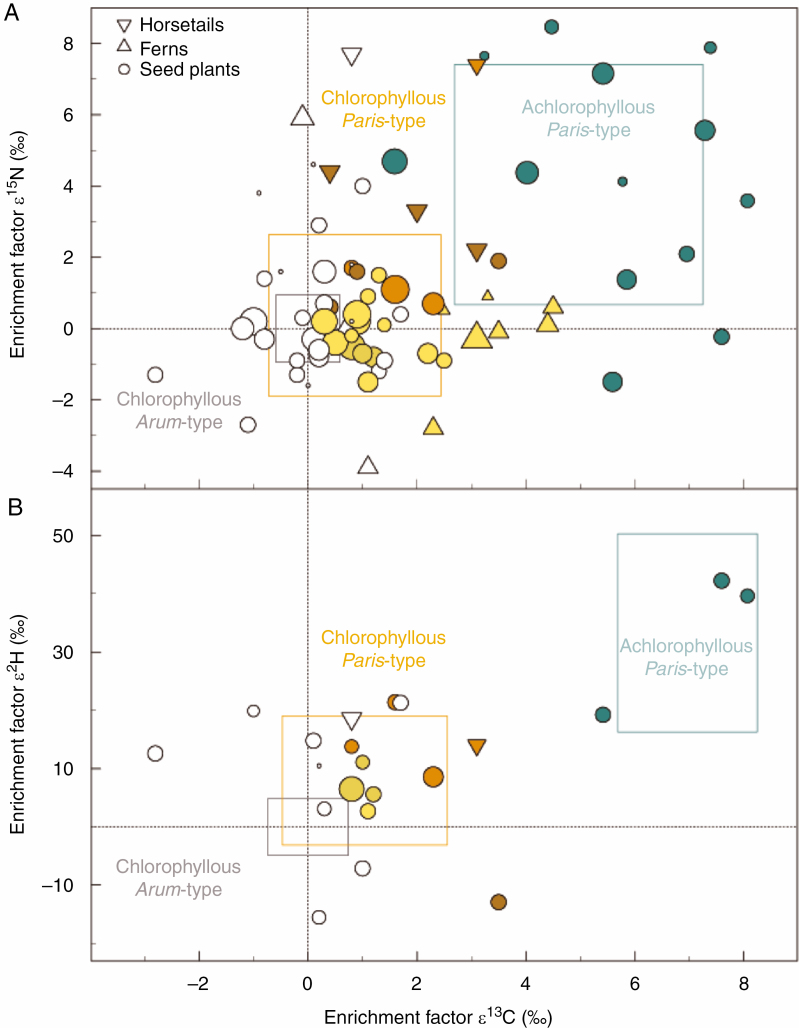
Fig. 1.
(A) Carbon and nitrogen enrichment factors (ε 13C and ε 15N) and (B) carbon and hydrogen enrichment factors (ε 13C and ε 2H) for chlorophyllous Arum-type arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) plant species (grey frame, s.d.), chlorophyllous Paris-type AM plant species (brownish tones, brown frame, s.d.) and achlorophyllous, full mycoheterotrophs on AM fungi (blue, blue frame, s.d.). AM morphotype assignment was obtained from the literature (see the Materials and Methods). Each species is represented by mean values and the s.d. is omitted for clarity. Symbol size reflects the sample size of the Paris-type species (n = 1–31, see Supplementary data Table S3). Each chlorophyllous Paris-type AM plant species was tested for significance of differences in ε 13C, ε 15N and ε 2H from co-occurring chlorophyllous Arum-type AM plant species (see Supplementary data Table S3). Chlorophyllous Paris-type AM plant species shown in coloured symbols are significant in at least one trait (13C enrichment, light gold; 13C + 2H enrichment, light brown; 13C + 15N enrichment, dark brown, 13C + 2H + 15N enrichment, dark gold; no significant enrichment, white). Achlorophyllous plant species were not included in the test procedure (see Gomes et al., 2020). The data comprise for 13C/15N: 13 achlorophyllous Paris-type species (n = 99), 63 chlorophyllous Paris-type species (n = 520) and 59 chlorophyllous Arum-type species (n = 530). The data comprise for 2H: three achlorophyllous species (n = 14), 18 chlorophyllous Paris-type species (n = 100) and 15 chlorophyllous Arum-type species (n = 104).