Figure 2.
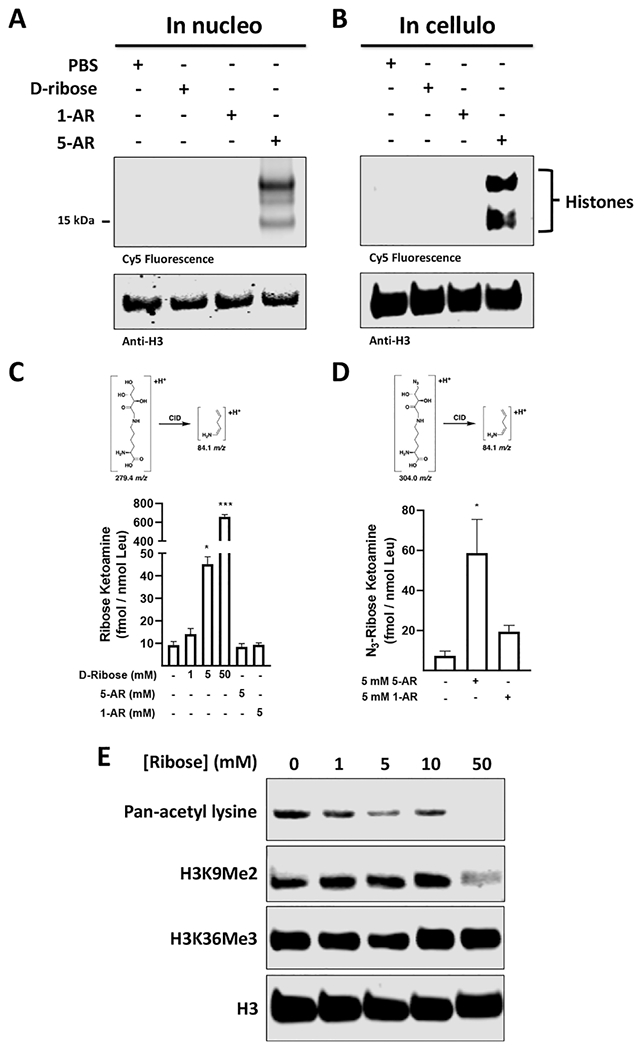
Ribose permeates cells and nuclei to glycate histones. (A) Glycation of isolated 293T nuclei with PBS or 5 mM of d-ribose, 1-AR, or 5-AR for 8 h, followed by DBCO Cy5 labeling and in-blot fluorescence visualization and western blot analysis. (B) Glycation of live 293T cells with PBS or 5 mM of d-ribose, 1-AR, or 5-AR, followed by hypotonic isolation of nuclei, DBCO Cy5 click labeling, in-blot fluorescence and western blot analysis. (C) Quantification of RiboLys on chromatin isolations from 293T cells incubated with 5-AR, 1-AR, or increasing concentrations of d-ribose. (D) Quantification of Az-RiboLys on chromatin isolations from 293T cells incubated with 5-AR or 1-AR. The MRM transitions used for quantification are shown. (E) Glycation of live 293T cells with increasing amounts of d-ribose followed by high-salt histone extraction, and western blot post-translational modification (PTM) analysis with the indicated antibodies.
