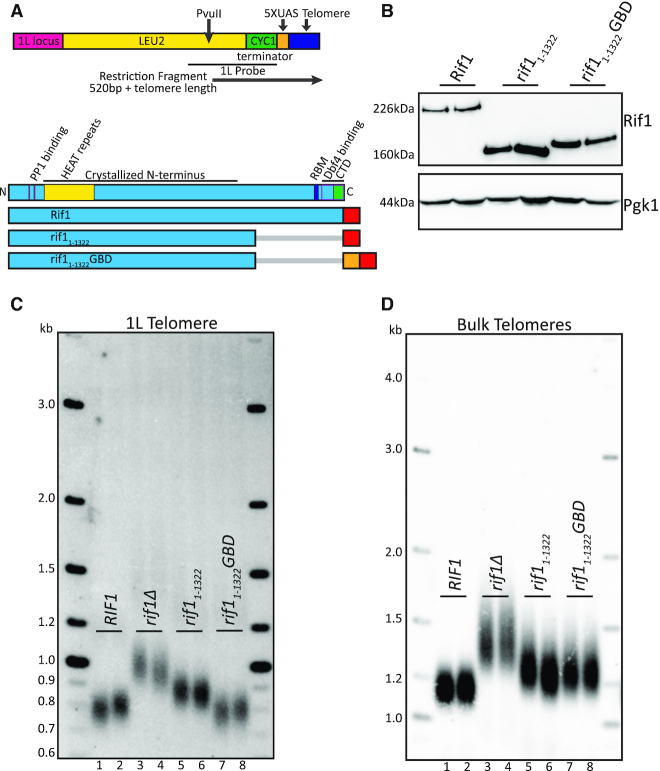
Figure 1.
Rif1 N-terminus when localized to telomere is functionally sufficient in telomere regulation. (A) Diagram of 5XUAS landing pad and evaluated Rif1 constructs. The 1L telomere restriction fragment is indicated by the black arrow below the diagram beginning at the PvuII cut-site. The lower section of the diagram shows a Rif1 domain map depicted to scale (RBM: Rap1 binding motif; CTD: Carboxyl-terminal domain; Dbf4 binding overlaps CTD). Below is a schematic of the Rif1 constructs tested in this figure (Blue: Rif1; Red: 6xFLAG; Orange: GBD; Gray bar: C-terminal truncation of residues). (B) Western blot showing Rif1 (anti-FLAG antibody) and Pgk1 (anti-Pgk1 antibody, control) protein levels of indicated strains. (C) Southern blot showing 1L telomere probe for the indicated strains. (D) Southern blot from C, rehybridized with a Y’ probe to visualize ‘bulk’ XhoI restriction fragments. For the Southern blots in (C and D), PvuII and XhoI were both used together to digest genomic DNA. The LEU2 gene was used as a probe to detect the PvuII restriction fragment of the unique 1L telomere (denoted in Figure 1A, primers in Supplementary Table S1) (See ‘Materials and Methods’ section).