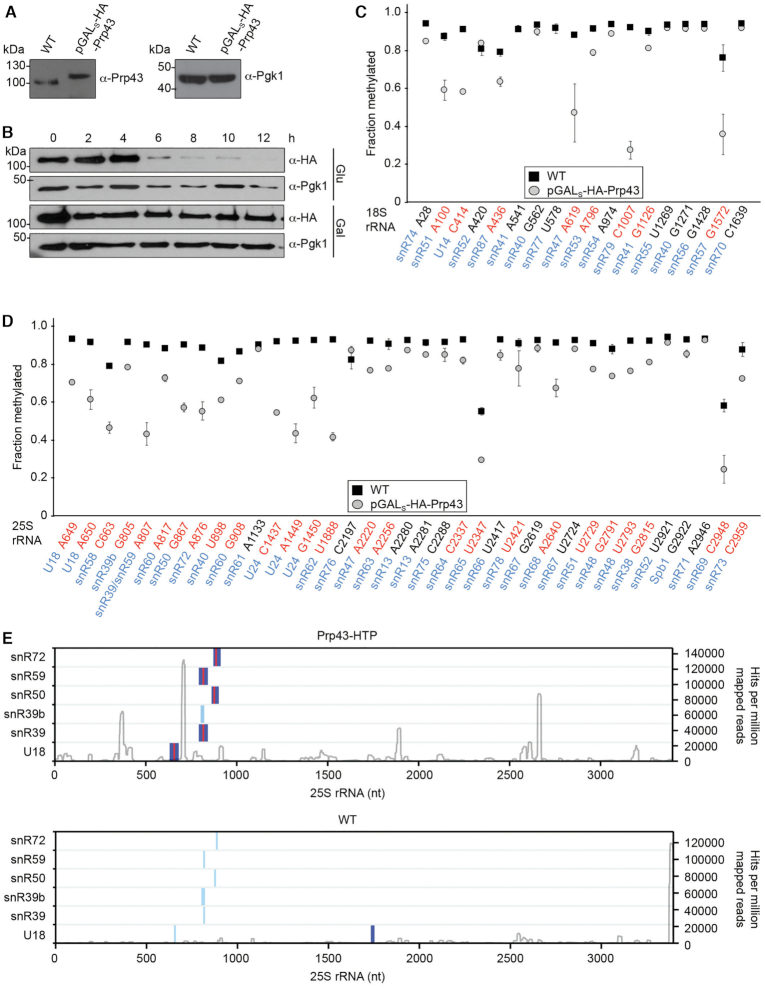
Figure 8.
Prp43 is required for efficient rRNA 2′-O-methylation and crosslinks to snoRNA–pre-rRNA duplexes. (A) Proteins from wild type yeast (WT) and the pGALS-HA-Prp43 strain grown in galactose-containing media were separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed using antibodies against Prp43 and, as a loading control, Pgk1. (B) The pGALS-HA-Prp43 strain was grown in exponential phase in media containing galactose (Gal) or glucose (Glu) for 12 h. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points, and proteins were extracted, separated by SDS-PAGE and analysed by western blotting using antibodies against the HA tag and Pgk1. (C, D) RiboMeth-seq analysis was performed on RNA derived from wild type yeast and the pGALS-HA-Prp43 strain grown exponentially in media containing glucose for 8 h. RiboMeth-seq scores, indicating the fraction of methylation, are plotted for each 2′-O-methylated nucleotide in the 18S rRNA (C) and the 25S rRNA (D). The data shown are the mean of two biological replicates and error bars represent standard deviation. The snoRNAs that guide each modification are indicated in blue and modifications for which the RMS score is decreased by >10% when Prp43 is depleted are highlighted in red. (E) The positions of predicted snoRNA basepairing sites (light blue) and chimeric reads identified in the Prp43 (upper) and WT (lower) CRAC datasets (26) by Hyb (dark blue) are mapped according to their positions on the 25S rRNA sequence. Sites of overlap between snoRNA basepairing sites and CLASH hybrids are shown in red. The profile of Prp43 crosslinking on the 25S rRNA sequence (28) is shown in grey with the peak heights given on the right.