Figure 3.
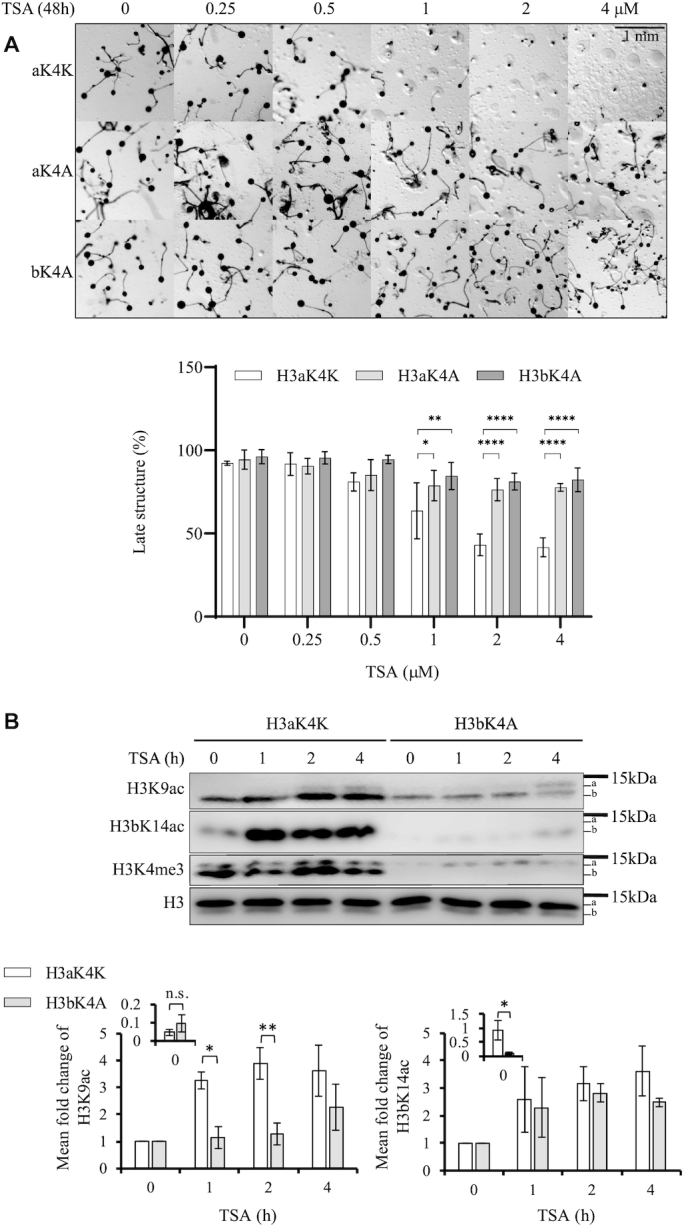
Loss of H3K4me3 delays H3 acetylation and confers developmental resistance to TSA. (A) H3aK4A and H3bK4A cells are resistant to TSA during development. H3aK4A, H3bK4A and control H3aK4K cells were washed with KK2 and allowed to develop on buffered agar in the presence of increasing concentrations of TSA as described in Figure 1A. Images were taken at 48 h and representative images of three repeats are presented. The percentage of late structures is shown as average ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using a two-way ANOVA with Tukey test. (B) TSA-induced increase of H3K9 acetylation is delayed in H3bK4A cells. Cells were washed with KK2 and developed in the presence or absence of 4 μM TSA for 0–4 h in KK2 before harvesting for acid-extraction. Acid-extracts were resolved by 18% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using specific antibodies as indicated. Results are presented as described in the legend to Figure 2B showing the mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using a Student's paired t-test. *P < 0.05; **P< 0.01; ****P< 0.0001.
