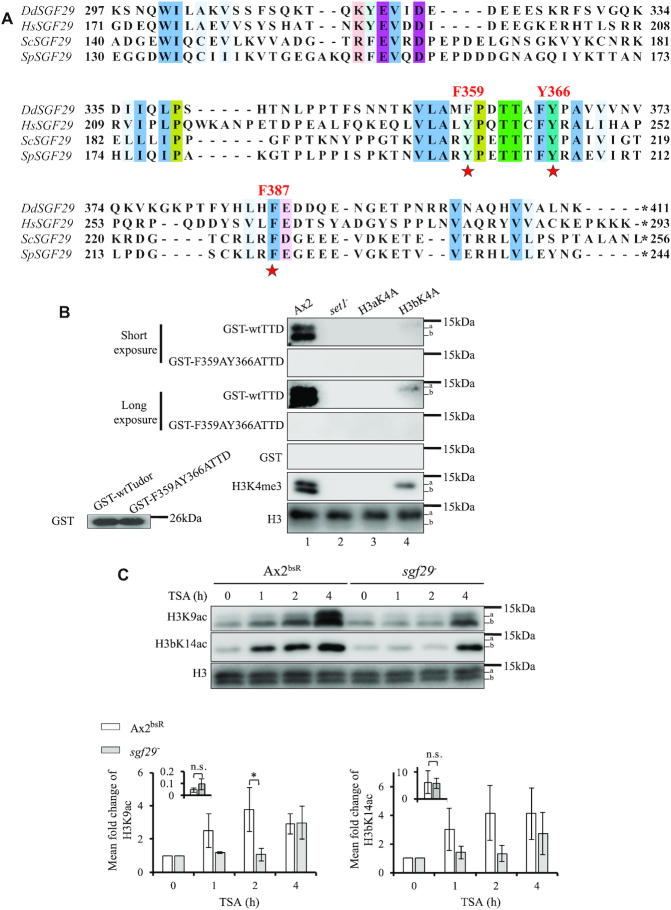
Figure 4.
TTD of Sgf29 recognizes H3K4me3 while deletion of the gene encoding Sgf29 delays the increase in H3 acetylation on TSA treatment. (A) A candidate Dictyostelium orthologue of Sgf29 (DdSgf29, 411 a.a.) contains conserved tandem Tudor domain (TTD). Protein sequence alignment of the TTDs of Sgf29 from budding yeast (Sc), fission yeast (Sp) and human (Hs) together with DdSgf29. Conserved residues binding the tri-methylated lysine are labelled with red asterisks and their positions relative to the initiating methionine are shown. *, stop codon. Clustal X Colour Scheme is used to indicate the conservation of amino acids. (B) The TTD interacts with H3K4me3-modified histones. Wildtype or F359AY366ATTD was expressed and purified from E. coli as GST-fusion proteins. Acid extracts were prepared from exponentially growing Ax2, set1–, H3aK4A and H3bK4A cells and resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane and incubated with the fusion proteins as indicated. The interaction between GST-fusion protein and histone H3 is detected using an anti-GST monoclonal antibody. GST alone was used as a negative control. Equal amounts of purified recombinant proteins were used as indicated by the lower left blot. Specific antibodies were used to detect H3K4me3 and histone H3. Representative blot shown (n = 3). (C) TSA-induced increase of H3K9 and H3bK14 acetylation are delayed in sgf29– cells. Control Ax2bsR cells (with random integration of the gene disruption vector) and sgf29– cells were washed with KK2 and developed in the presence or absence of 4 μM TSA for 0–4 h in KK2 before harvesting for acid-extraction. Acid-extracts were resolved in 18% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using specific antibodies as indicated. The mean levels ± SD of H3K9Ac and H3bK14Ac from three independent experiments are presented as described in the legend to Figure 2B. Statistical significance was calculated using a Student's paired t-test. *P< 0.05.