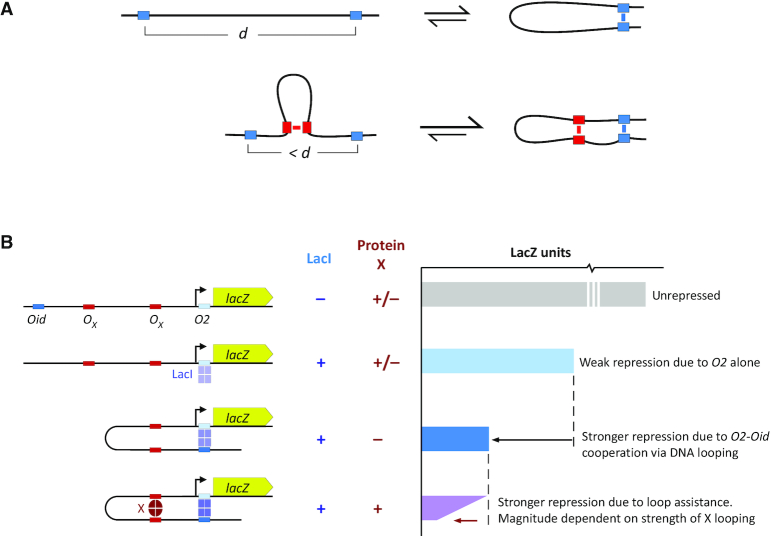
Figure 1.
Assaying DNA looping by loop assistance. (A) The DNA loop formed between an internal pair of sites (red) assists the formation of the loop between the external sites (blue) by reducing the effective DNA distance, d, between them. (B) DNA looping by a candidate protein (X) and its DNA-binding sites (OX) is detected and measured in the loopometer by its enhancement of loop-dependent LacI repression of a promoter for a lacZ reporter. In the absence of the strong upstream lacOid operator, a LacI tetramer binds poorly to the weak lacO2 operator, giving weak repression of the promoter. In the presence of Oid, occupation of O2 is increased due to cooperative DNA looping, and repression is increased. DNA looping by the candidate protein shortens the distance between Oid and O2, increasing LacI looping and further improving repression.