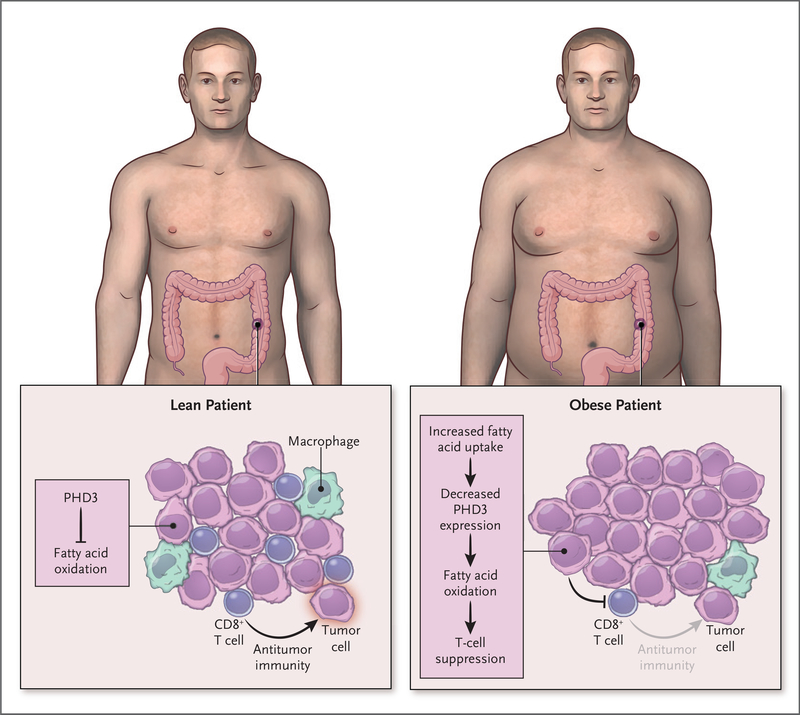
Figure 1. Obesity and the Tumor Immune Microenvironment.
Obesity reshapes the metabolism of cancer cells to impair T-cell inflammatory functions. Obesity remodels the cellular fuel use of tumors to increase cancer-cell fatty acid oxidation while reducing the numbers and spatial positioning of CD8+ T cells to reduce antitumor immunity. A “multi-omic” approach showed that PHD3 is a candidate to mediate these effects because decreased PHD3 expression led to greater lipid metabolism and T-cell suppression.