Figure 1. Canonical and non-canonical synapse types.
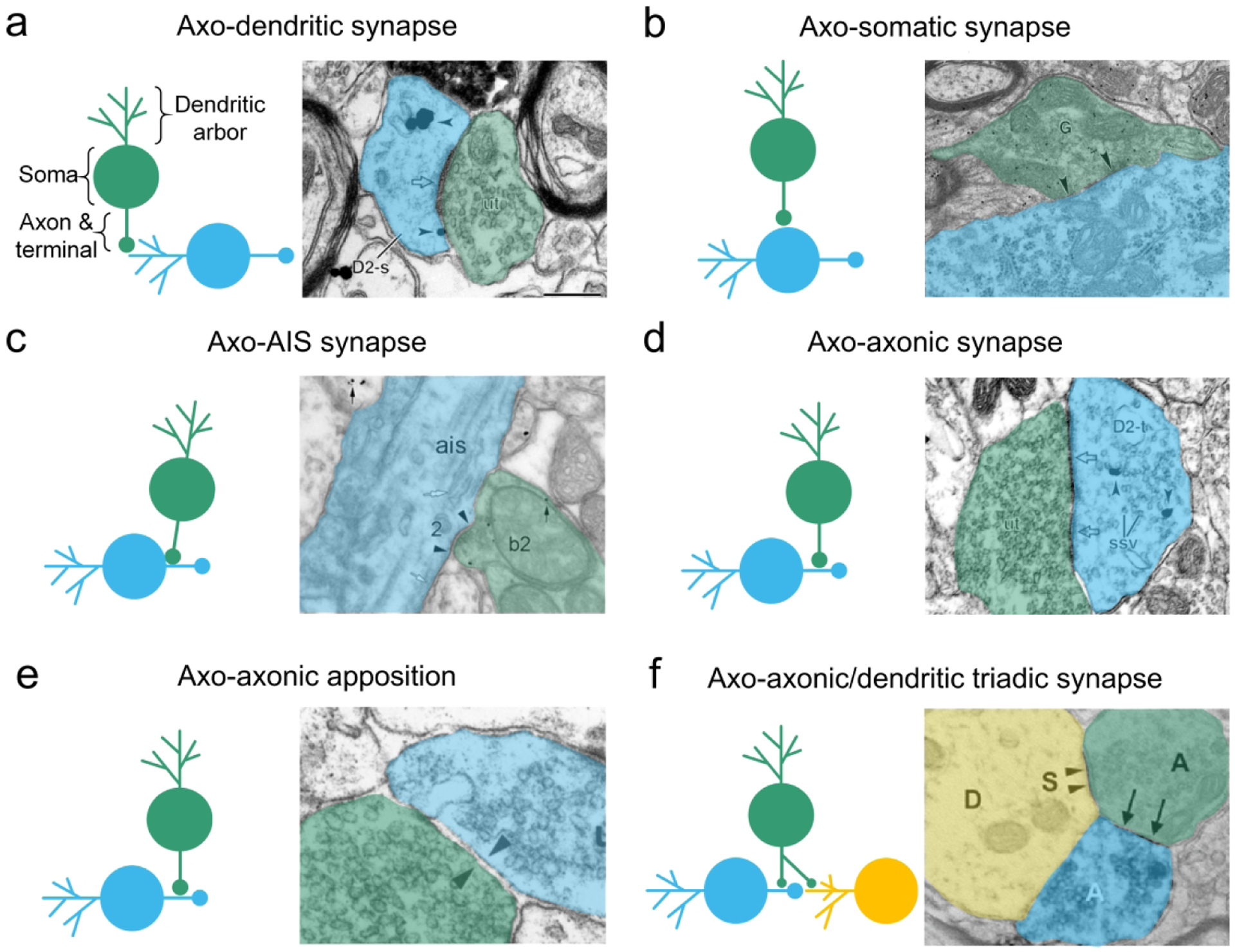
Four common synaptic arrangements between presynaptic (green) and postsynaptic (blue) neurons are depicted through schematic illustrations (left) and electron micrographs (right). a. The axo-dendritic synapse consists of the presynaptic axon terminal (green) synapsing on a dendritic element (i.e. spine or shaft) of the postsynaptic cell (blue). b. The axo-somatic synapse is comprised of a presynaptic axon (green) terminating on the cell body of the postsynaptic neuron (blue). c. An axon (green) may terminate on the axon initial segment (AIS) to modulate action potential generation of the postsynaptic neuron (blue). d. In an axo-axonic synapse, the presynaptic neuron (green) synapses on an axon or axon terminal of the postsynaptic cell (blue). e. Axo-axonic appositions describe closely apposed axon terminals with parallel membranes separated by a clear cleft and lack densities associated with synaptic elements. Note that the directionality of such synapses is often unclear, as is the case for the present example. f. The axo-axonic triad describes a configuration in which a neuron (green) synapses on both the presynaptic element (blue) and postsynaptic target (yellow) of an axo-dendritic or – somatic synapse. Electron micrographs are adapted from Wang & Pickel, 2002 (a, d), Lue, et al., 1997 (b), Takács et al., 2015 (c); Sesack & Pickel, 1990 (e), and Soiza-Reilly et al., 2013 (f).
