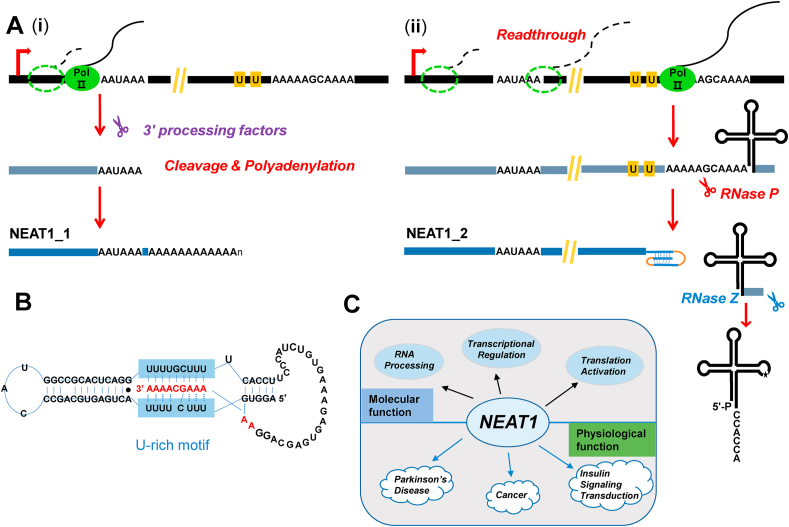
Fig. 2.
The biogenesis, structure, and functions of NEAT1. (A)NEAT1_1 (the short form of NEAT1) is stabilized by a canonical poly(A) tail following cleavage/polyadenylation. However, NEAT1_2 (the long form of NEAT1) undergoes steps similar to that of MALAT1 biogenesis. (B) The A- and U-rich motifs, present upstream of the RNase P cleavage site, form a triple helix via base-pairing, protecting the 3′ end of NEAT1_2 from degradation. Figure is adapted from Ref. [6]. (C)NEAT1 is involved in diverse molecular events, such as RNA processing and transcriptional regulation. The dysregulation of NEAT1 contributes to many diseases.