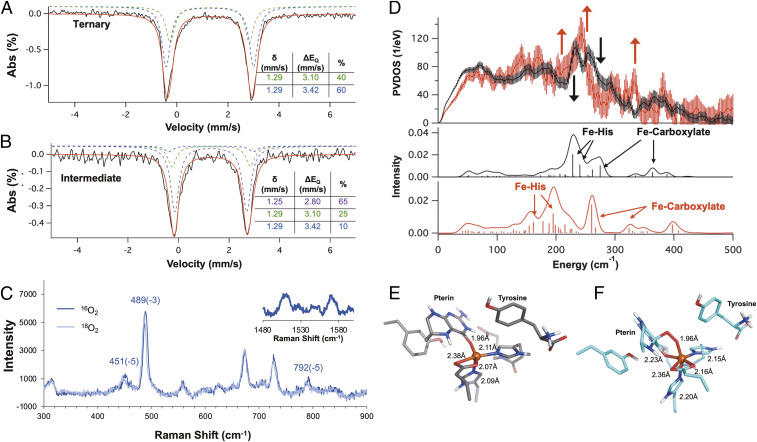
Fig. 3.
Mössbauer spectra of the (A) ternary complex and (B) the 442 nm pre-FeIV = O intermediate generated by reacting 0.5 mM (FeII/BH4/Trp)-TPH with 1 mM O2 in Hepes/(NH4)2SO4/sucrose buffer (pD 7). The parameters for the ternary complex and the intermediate are listed in their respective tables. (C) Resonance Raman spectra using the 457.9 nm laser line of the 442 nm intermediate (0.5 mM (FeII/BH4/Trp)-TPH + 1 mM O2) rapid-freeze quenched at 150 ms. (Inset) Raman shifts measured in the 1,480 to 1,610 cm−1 region showing resonance enhanced features at 1,514 and 1,570 cm−1. The change in the energies of the vibrations from the 16O2/18O2 isotope perturbation are indicated. Note that the 1,514 and 1,570 cm−1 features do not show an O2 isotope effect. (D, Top) NRVS spectra of the ternary FeII complex (black) and the rapid freeze quenched intermediate (red, 1 mM (FeII/BH4/Trp)-TPH + 1 mM O2). The error bars in the processed spectra are represented by vertical lines. The contribution of the ternary complex to the intermediate spectrum was removed and the spectrum renormalized as described in SI Appendix, Fig. S22. The black arrow depicts loss of intensity, while the red arrows show gain in intensity going from the ternary FeII complex to the intermediate spectrum. (Bottom) Simulation of NRVS spectra of the ternary complex (black) and the peroxy intermediate (red) with the pterin carbonyl bound to the FeII center. Optimized structures of (E) the ternary complex and the (F) peroxy intermediate with the pterin carbonyl bound. The metal–ligand distances are indicated.