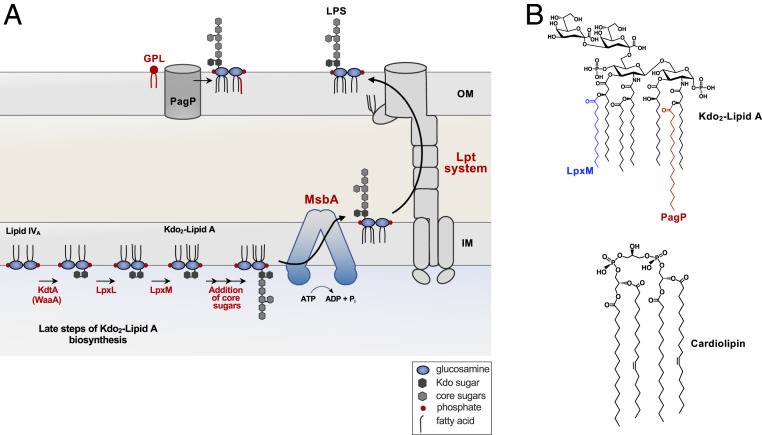
Fig. 1.
Biosynthesis and transport of LPS. (A) The latter steps of Kdo2-lipid A biosynthesis catalyzed by KdtA (WaaA), LpxL, and LpxM are shown. Two Kdo sugars are added to the tetra-acylated lipid A precursor, termed lipid IVA. The Kdo sugars are part of the core oligosaccharide and are required for the ordered addition of last two acyl chains by LpxL and LpxM. First, LpxL adds a laurate (C12:0) followed by LpxM that adds a myristate (C14:0) group forming hexa-acylated Kdo2-lipid A. The remaining core oligosaccharide is extended at the cytoplasmic face of the IM, requiring various glycosyl transferase (not shown). MsbA, an ABC transporter, flips the core–lipid A structure to the periplasmic face of the IM. For simplicity, the O-antigen addition is not shown and is absent in E. coli K-12 strains. The intermembrane translocation of LPS to the OM is conducted by the Lpt system, which forms an envelope-spanning translocation machine. PagP, an OM protein, transfers a palmitate (C16:0) group from mislocalized GPL (red) in the outer leaflet of the OM to LPS. (B, Top) Chemical structure of Kdo2-lipid A with the acyl chain added by LpxM in blue, and the chain added by PagP is in red. (B, Bottom) Structure of cardiolipin.