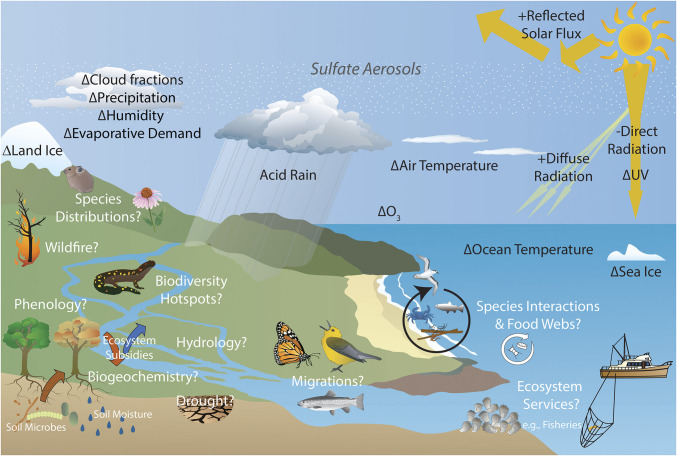
Fig. 1.
Although some effects of SRM with SAI on the climate are known from certain SAI scenarios (indicated with + for likely increases, − for decreases, Δ to indicate change), the effects of SAI on ecological systems are largely unknown. Such biotic and abiotic changes would vary across Earth and depend on the SAI scenario. Stratospheric aerosols from SAI would reflect more sunlight—including UV radiation—to space, reducing surface UV. SAI could also destroy stratospheric ozone, increasing surface UV (Fig. 2A). The net effects of SAI on UV and ozone depend on the amount and distribution of aerosols in the stratosphere, the type of aerosols used, and how the aerosols interact with the chemistry and radiation of the atmosphere (e.g., refs. 23 and 141). Potential changes in ocean temperature and ocean pH in different regions are illustrated below (Fig. 3). Symbols courtesy of the Integration and Application Network, University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science (https://ian.umces.edu/symbols/).