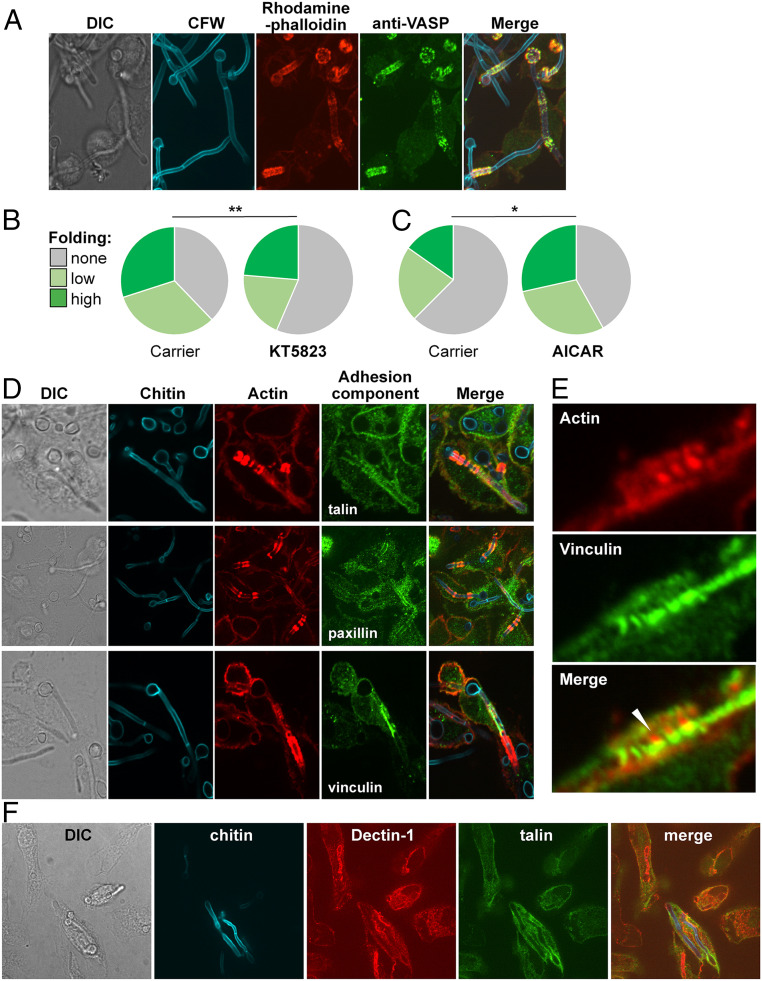
Fig. 4.
Podosome components associated with phagocytosed hyphae. (A) VASP (anti-VASP antibody, green) colocalizes with actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red) on BMDM phagosomes containing live C. albicans SC5413 (Calcofluor White; CFW, blue). Cells were fixed after 4 h of C. albicans–BMDM interactions and subjected to phase differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence microscopy. (B) Pretreating BMDMs with KT5823 (0.1 µM), which reduces phosphoVASP levels, decreases their folding of fixed tup1Δ hyphae (n = 160) compared with the ethyl acetate carrier control (n = 186): unfolded cells (gray); hyphae displaying moderate bending (obtuse angle; pale green); hyphae displaying (acute angle; dark green). (C) Preincubating with AICAR (0.3 mM), which increases phosphoVASP levels, enhances the ability of BMDMs to fold tup1Δ hyphae (n = 145) compared with the H2O2 carrier control (n = 139). The data for each experiment are from three independent analyses with BMDMs from different mice. Statistical comparisons were made using a χ2 test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (D) Podosomal components localize with actin rings around phagosomes containing live C. albicans SC5314 hyphae. Three independent examples of this colocalization are shown: phase DIC microscopy, fungal chitin (CFW, blue), BMDM actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red), talin (anti-talin antibody, green; Top), paxillin (anti-paxillin antibody, green; Middle), and vinculin (anti-vinculin antibody, green; Lower). (E) A close-up showing juxtaposition of actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red) and vinculin (anti-vinculin antibody, green) on a BMDM phagosome containing a C. albicans SC5314 hypha. (F) Colocalization of Dectin-1 (anti-Dectin-1, red) and talin (anti-talin antibody, green) on BMDM phagosomes containing C. albicans SC5314 hyphae (chitin stained with CFW, blue).