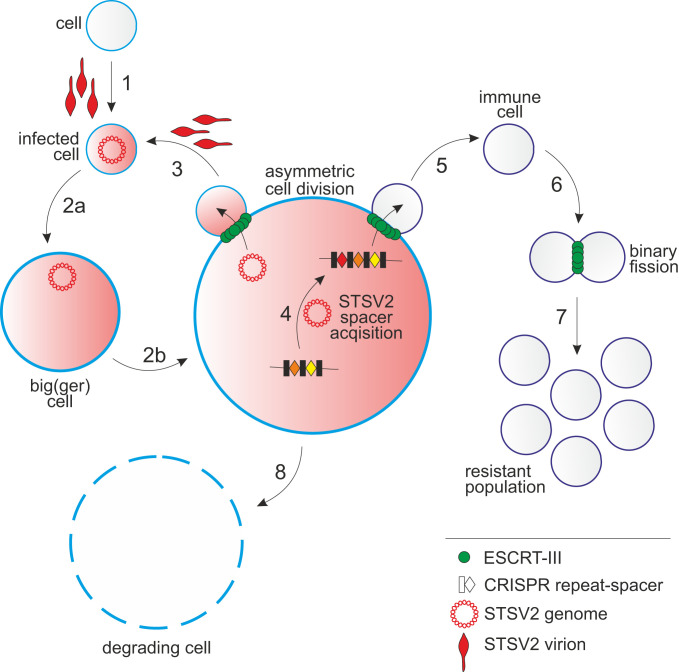
Fig. 6.
A schematic representation of the STSV2-Sulfolobus interactions. 1: infection of a normal-sized cell; 2a and 2b: gradual increase in the diameter of STSV2-infected cells; 3: asymmetric division of a STSV2-infected giant cell leading to the budding of a normal-sized cell, which can be reinfected (by exogenous virus or by virus genome vertically transmitted from the giant cell) to restart the cycle; 4: acquisition of CRISPR spacers against STSV2; 5: asymmetric division of a STSV2-infected giant cell leading to the budding of a normal-sized cell resistant to STSV2 infection due to the presence of CRISPR spacers against STSV2; 6: division of the STSV2-resistant cells by binary fission; 7: proliferation of the resistant population; and 8: gradual decay of the giant cell.