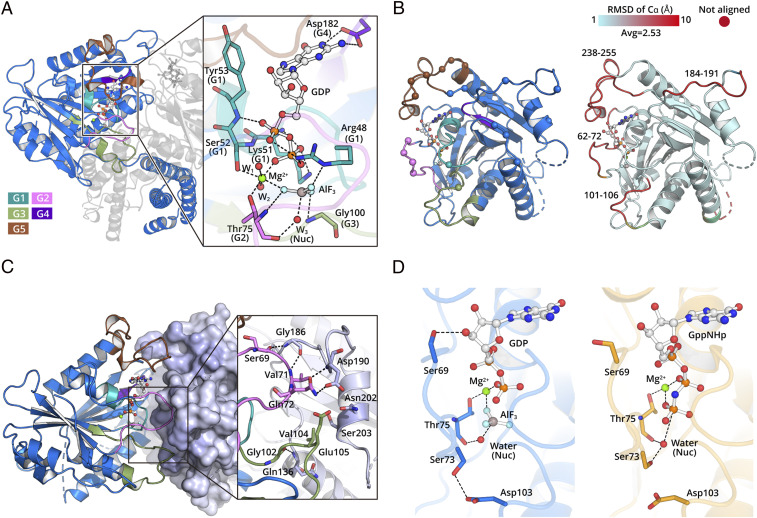
Fig. 2.
The hGBP5 LG domain forms a dimer during GTP hydrolysis. (A) The hGBP5 LG domain binds GTP using canonical motifs depicted in different colors. The residues directly interacting with GDP ⋅ AlF3 are shown as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dotted lines. (B) LG domain dimer interface. Residues directly involved in intermolecular interactions are shown as spheres (Left). Conformational changes induced by nucleotide are colored by RMSD (Right). (C) The conserved nucleotide hydrolysis motifs are located at the LG domain dimer interface and directly mediate intermolecular interactions. A representative region at the interface is shown in the inset. (D) The nucleotide hydrolysis mode is slightly different between hGBP5 (Left) and hGBP1 (Right).